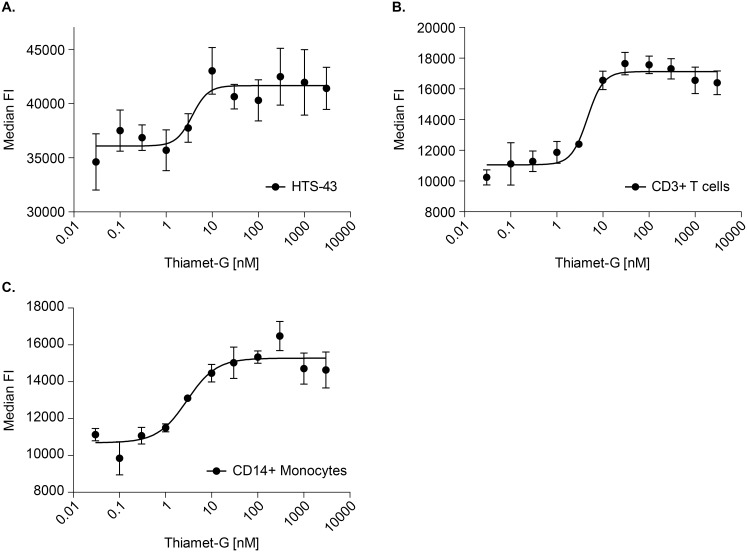
Fig 1. Inhibition of O-GlcNAcase by thiamet -G increases O-GlcNAcylated protein levels in CD3+ T-cells, CD14+ monocytes and HTS-43 cells.
(a). HTS-32 cells (CD14+) were incubated overnight at varying concentrations of thiamet-G. The cells were then stained with a custom Alexa-fluor 647 RL2 antibody to detect O-GlcNAac levels via flow cytometry, with units being representative as median fluorescent intensity. (b,c) PBMCs were incubated with varying concentrations of thiamet-G overnight. The cells were stained for monocytes (CD14+/CD3-) and T-lymphocytes (CD3+/CD14-) and then stained with the RL2 antibody for O-GlcNAc detection. Units were measured as mean fluorescence intensity. Data points represent n = 3. Error bars represent standard deviation.