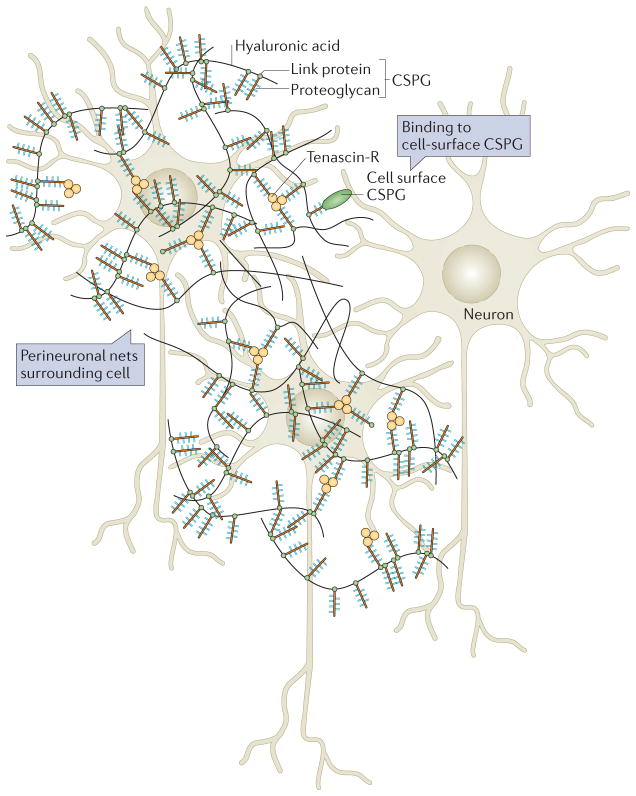
Figure 5. Perineuronal nets.
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) surround cells of the brain and act as inhibitors of both growth and migration. PNNs are lattices of hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans and tenascin molecules. The basic structure of a PNN is depicted here. Hyaluronic acid chains coated with proteoglycans are linked by trimeric tenascin R molecules to form a fairly organized structure around neurons. The chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans (CSPGs) within the net bind to cell surface CSPGs and can thus control cell behaviour. Figure modified from REF. 115, Nature Publishing Group.