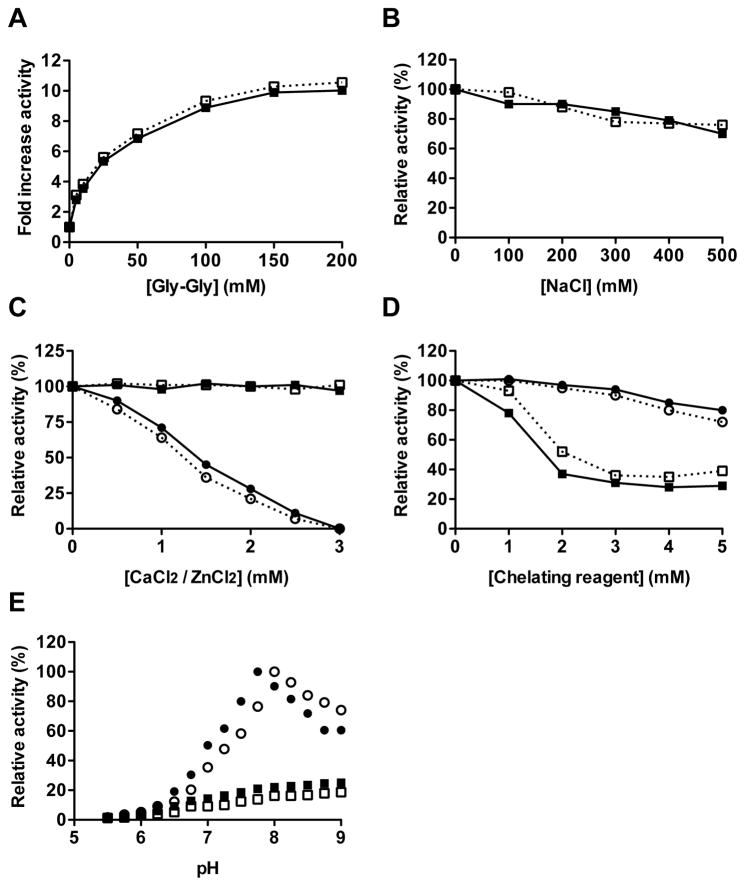
Figure 3.
Comparison of activity of RgpB-6His and native RgpB in various conditions. The amidolytic activities of Rgp-6His (open symbols) and native RgpB (filled symbols) were determined at 37°C using the chromogenic substrate L-BAPNA (λ = 405 nm; n = 3) in activity assay buffer (200 mM Tris, 10 mM L-cysteine, pH 7.6) supplemented with increasing concentration of: the dipeptide Gly-Gly (A); NaCl (B); divalent cations Ca2+ (square) or Zn2+ (circle) (C); and the chelating reagents EDTA (square) and 1,10 orthophenanthroline (circle) (D). Alternatively, the effect of the pH on the amidolytic activity was determined in 0.1 M Tris, 0.05 M MES and 0.05 M acetic acid buffer adjusted from pH 5 to 9 with (circle) or without (square) 50 mM Gly-Gly (E).