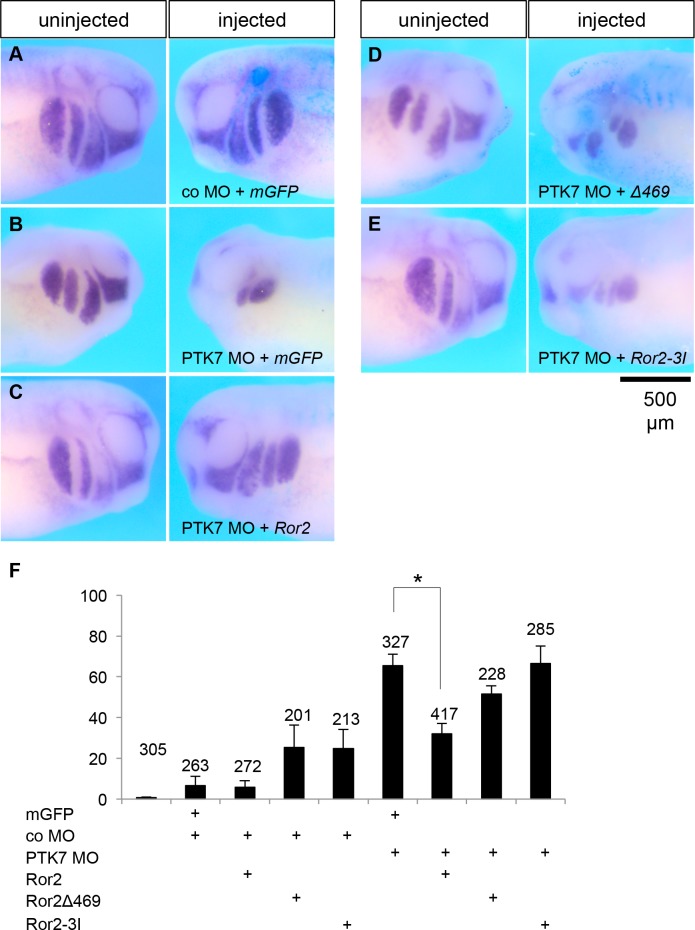
Fig 5. The kinase domain of Ror2 is required to rescue the NC migration defect in PTK7 morphant embryos.
Xenopus embryos were injected with different constructs in combination with 100 pg LacZ RNA as a lineage tracer and analyzed by whole-mount in situ hybridization using a twist antisense RNA probe. A Embryo injected with 10 ng control MO and 100 pg GFP RNA shows normal NC migration. B Embryo injected with 10 ng PTK7 MO and 100 pg GFP RNA shows inhibition of NC migration on the injected side, while NC migration is normal on the uninjected side. C Co-injection of 10 ng PTK7 MO together with 100 pg Ror2 RNA rescues the NC migration defect. D Embryo injected with 10 ng PTK7 MO and 100 pg of Ror2Δ469 RNA. The embryo shows a NC migration defect on the injected side. E Embryo injected with PTK7 MO and a kinase dead mutant of Ror2 (Ror2-3I) showing a NC migration defect on the injected side. F Graph summarizing the percentage of NC migration defects of a minimum of 5 independent experiments for each experimental condition. Asterisks indicates a p-value in a Student’s t-test < 0.001. Scale bar = 500 μm.