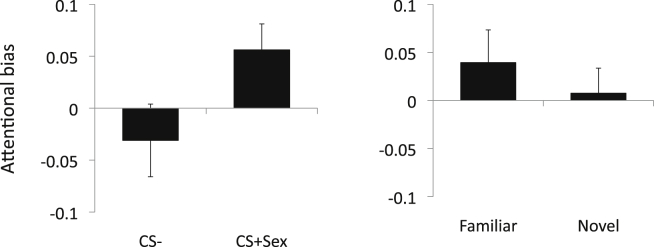
Fig. 2.
Relationship between choice preferences and attentional bias across groups. The left graph shows early attentional bias scores for sexual versus neutral stimuli (higher scores indicated greater bias towards sexual versus neutral stimuli) in subjects who preferred the CS+Sex as compared to CS− as the first choice across both groups. *p < 0.05. The right graph shows early attentional bias scores for sexual versus neutral stimuli in subjects who preferred the novel sexual stimulus as compared to the familiar stimulus.