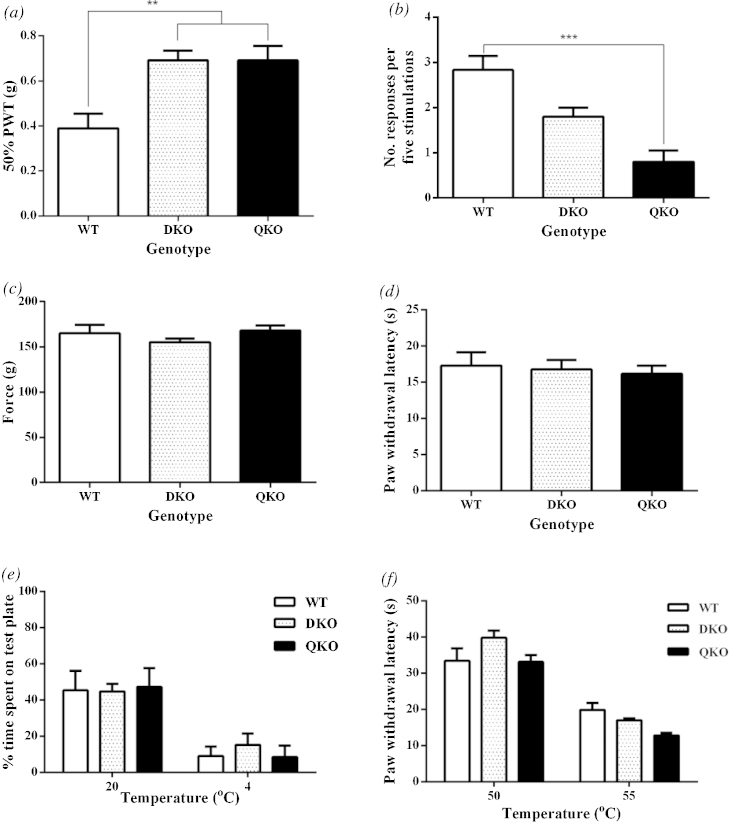
Fig. 1.
Modality specific sensory deficits in multiple KO animals. (a) DKO (0.69 g ± 0.04 g) (n = 10) and QuadKO (0.69 g ± 0.06 g) (n = 10) show an increase in 50% withdrawal threshold compared to WT (0.39 g ± 0.06 g) (n = 10) but no difference is seen between the two test groups. (b) QuadKO (0.8 ± 0.25) (n = 10) show a stepwise decrease in the percentage responses to a dynamic cotton swab stimulus compared to WT (2.83 ± 0.31) (n = 6) and DKO (1.8 ± 0.2) (n = 10). (c) No difference was observed in sensitivity to noxious mechanical force between groups (WT n = 6, DKO n = 10, QuadKO n = 10). (d) No difference was observed in sensitivity to noxious heat between groups (n = 6 all groups). (e) No difference was observed in sensitivity to a hot plate between groups (n = 6 all groups). (f) No difference was observed between groups of the time spent on a noxious cold plate (4 °C) following an acclimatisation session (20 °C) (n = 6 all groups). Data are shown as Mean ± SEM with one-way ANOVA with Tukey post test (a,c,d); Kruskal Wallis Test with Dunn’s post test (b) and two-way ANOVA with Tukey post test (e,f) *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.