FIGURE 8.
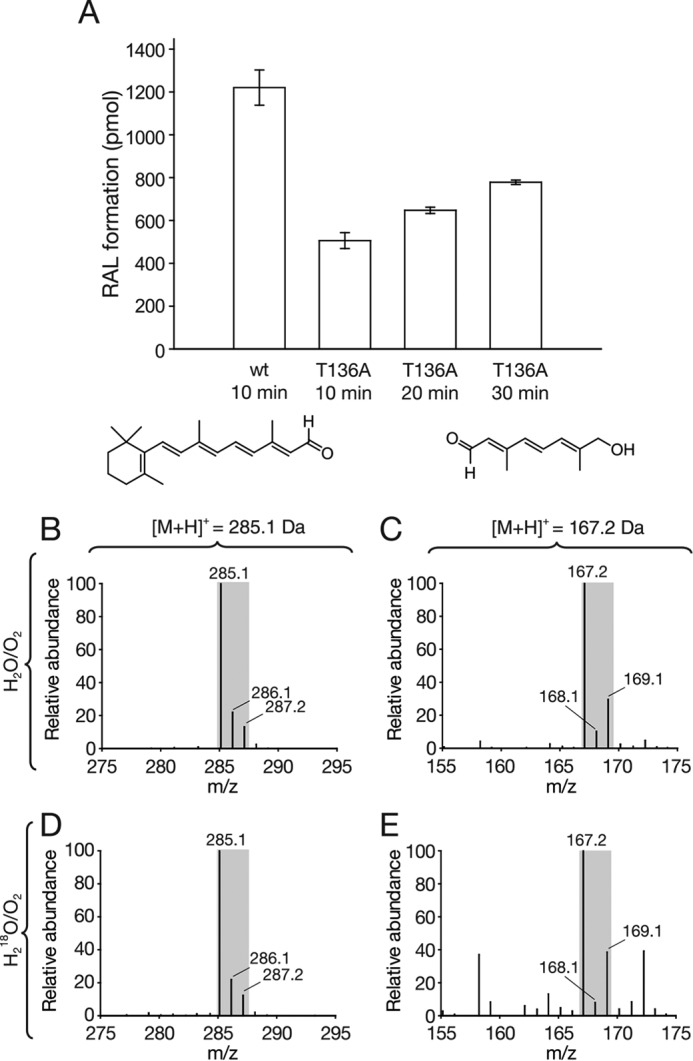
Activity and in vitro isotope-labeling analysis of T136A-ACO. A, activity results of T136A and wild-type ACO. 100 μg of purified protein were used in each reaction. Enzyme activity was assessed by following the formation of RAL over time. Note that the substrate is completely consumed by the wild-type protein within the 1st min of the reaction; therefore, product formation in this graph cannot be used to compare the activity levels of wild-type and T136A ACO. Error bars represent S.D.s calculated from triplicate measurements. B and C, mass spectra of apocarotenoid products generated by wild-type ACO in an H218O/16O2 environment. Note the increased levels of 18O-labeled RAL (m/z = 287.2) and C10-apocarotenal (m/z = 169.1) generated as a result of the high protein concentration used in the assay. D and E, mass spectra of apocarotenoid products generated by T136A-ACO in an H218O/16O2 environment were highly similar to those in B and C, which indicates preservation of dioxygenase activity in the ACO point mutant.
