FIGURE 7.
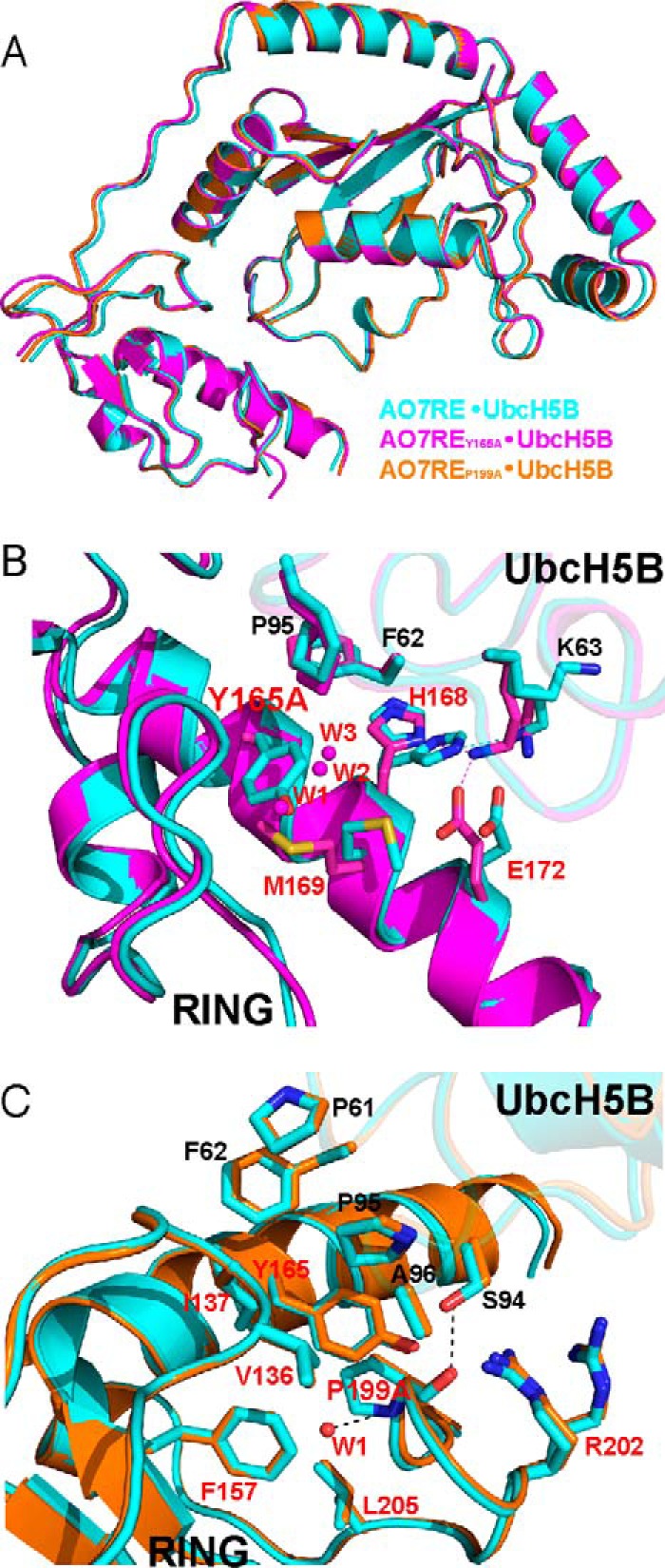
Structures of UbcH5B in complex with AO7RE mutants. A, superimposition of the AO7RE·UbcH5B (in cyan), AO7REY165A·UbcH5B (in magenta), and AO7REP199A·UbcH5B (in orange) complexes. B, the Y165A mutation resulted in a change in the AO7 Met-169 side-chain orientation inasmuch as the Met-169 side chain partially occupies the space created by the Y165A mutation, causing the AO7 Glu-172 side chain to bend toward the Met-169 side chain such that Glu-172 forms a new salt bridge with Lys-63 in the β3β4 loop of UbcH5B. The His-168 side chain, which is disordered in the WT, is stabilized in the mutant. Such conformational changes reshape the local E2-binding surface of the RING. Furthermore, several water molecules (W1, W2, and W3) invade into the cavity created by the Y165A mutation. The mutant and WT structures are shown in magenta and cyan, respectively. Residues at the RING-E2 interface are shown as sticks. The water molecules are shown as spheres. C, the P199A mutation brings a water molecule (W1) into the hydrophobic core of AO7 RING, which is hydrogen-bonded to the main chain amide of the Ala-199 residue. This does not disturb the conformation of nearby side chains. The residues on the interface or surrounding the hydrophobic core and the water molecule are illustrated. The mutant and WT structures are shown in orange and cyan, respectively.
