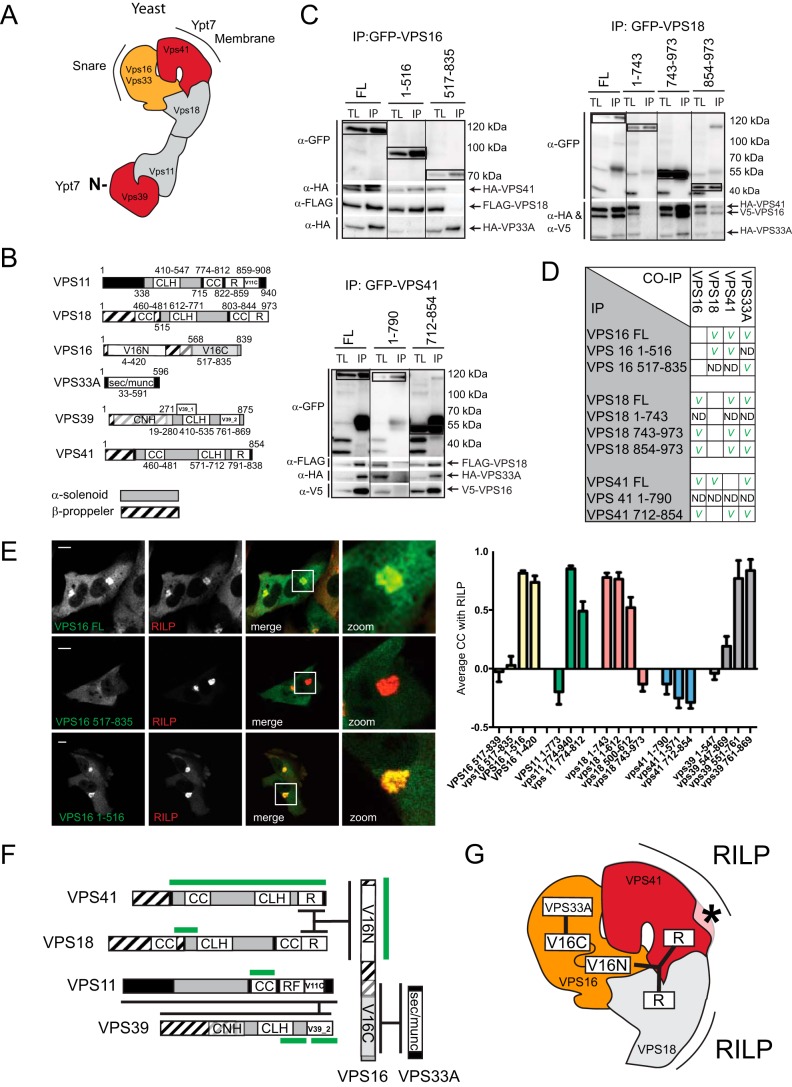
FIGURE 2.
Interactions within the mammalian HOPS complex. A, structure of the yeast HOPS complex. Yeast HOPS interacts with Ypt-7 via Vps41 and the N terminus of Vps39. B, domain organization of the mammalian HOPS complex subunit orthologs. CLH, clathrin heavy chain repeat; CC, coiled coil; R, ring finger; V11C, PFAM VPS11 C terminus; V16N, PFAM VPS11 N terminus; V16C, PFAM VPS11 C terminus; V39_1, VPS39 domain 1; V39_2, VPS39 domain 2; CNH, citron homology. C, lysates of MelJuSo cells co-expressing tagged VPS constructs as indicated were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-GFP antibodies and analyzed by WB using anti-HA, anti-FLAG, anti-V5, and anti-GFP antibodies as indicated. Within each panel, experimental conditions were run on the same blot with the same exposures for each detection antibody, and cutouts were taken and grouped for presentation purposes. D, summarized results of Fig. 2C. E, MelJuSo cells expressing GFP-VPS16 constructs (green) and mRFP-RILP (red). Scale bars: 10 μm. Graphs show average correlation coefficient (CC) ± S.E. n > 25, between different VPS truncation constructs and RILP. F, detailed map of domain interactions and membrane targeting modules (domains required for RILP binding are in green) within the mammalian HOPS complex. G, interactions in the head domain of the mammalian HOPS complex superimposed on the known structure of the yeast HOPS complex. Asterisk indicates functional divergence (absence of lipid binding motif in mammalian VPS41) between yeast and mammalian HOPS.