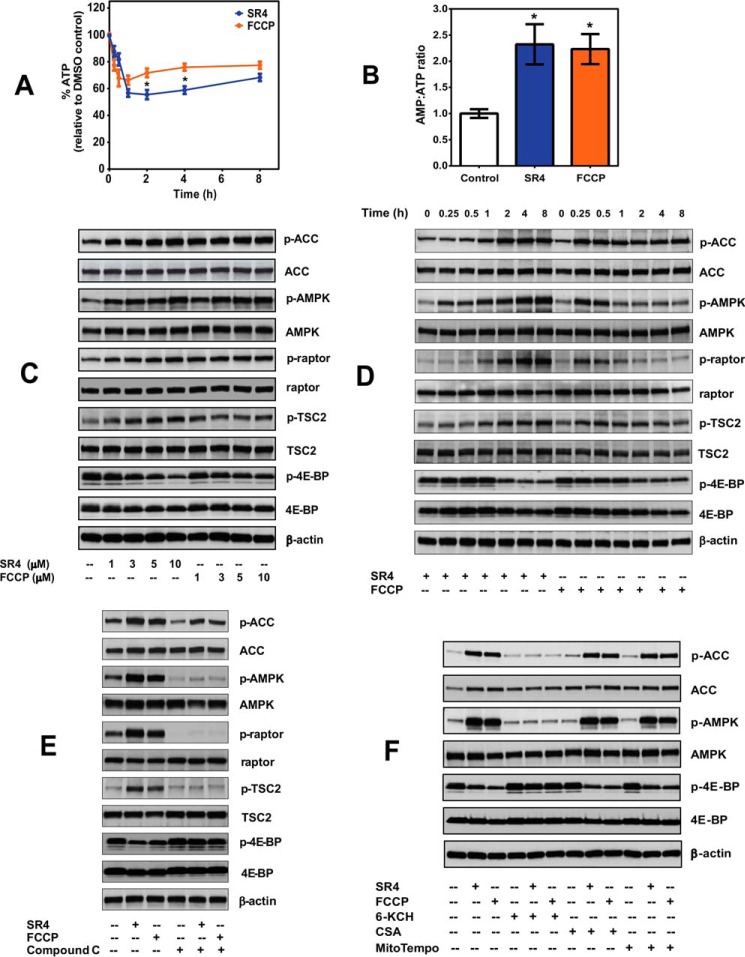
FIGURE 6.
SR4 decreases intracellular ATP production and modulates AMPK-mTOR signaling in HepG2. A, total intracellular ATP production in cells treated with either 5 μm SR4 or FCCP was measured by bioluminescence assay and expressed as a percentage of time-matched vehicle (DMSO) control. *, p < 0.05 versus FCCP by two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post hoc test. B, intracellular AMP/ATP ratios in HepG2 cells following 1 h treatment with either 5 μm SR4 or FCCP. *, p < 0.05 versus DMSO control (unpaired t test). C and D, representative Western blots analyses showing dose- and time-dependent modulation of the AMPK-mTOR signaling pathways in HepG2 cells. E, effects of the AMPK inhibitor Compound C on SR4 and FCCP-mediated AMPK-mTOR signaling. Cells were pretreated for 30 min with Compound C, followed by the addition of either 5 μm SR4 or FCCP for 4 h. F, effects of 6-KCH, CSA, and MitoTempo on SR4/FCCP-mediated AMPK activation. HepG2 cells were pretreated with 6-KCH (200 mm), CSA (1 μm), and MitoTempo (5 μm) for 15 min before the addition of SR4 (5 μm) or FCCP (5 μm). For all blots, total cell lysates treated without or with test compounds for the indicated times were resolved under electrophoresis and immunoblotted with antibodies against phosphorylated and total AMPK, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, raptor, TSC2, 4E-BP, and β-actin, which served as an internal control. Error bars, S.E.