FIGURE 6.
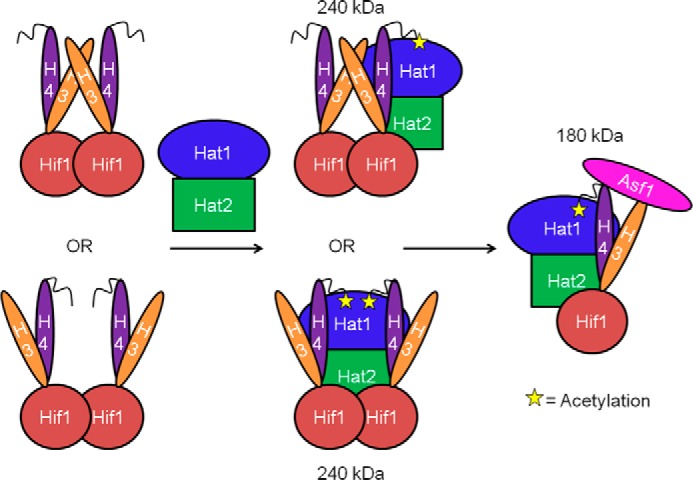
A model for participation of Hat1, Hat2, Hif1, and Asf1 in histone H3-H4 deposition. Hif1 is responsible for recruiting newly synthesized histones H3-H4 heteromers into HAT-B for acetylation. It is likely that Hif1 forms a dimer and binds to two copies of an H3-H4 dimer (as two heterodimers or one heterotetramer). Hif1 then brings the histones to the HAT-B complex for acetylation where the tails and cores of H3 and H4 make direct contact with both Hat1 and Hat2. This results in a complex with one Hat1, one Hat2, and two Hif1/H3-H4 molecules. After acetylation, Asf1 binds to the tetrameric interface of H3-H4 prior to H3-H4 transport into the nucleus for histone deposition into chromatin.
