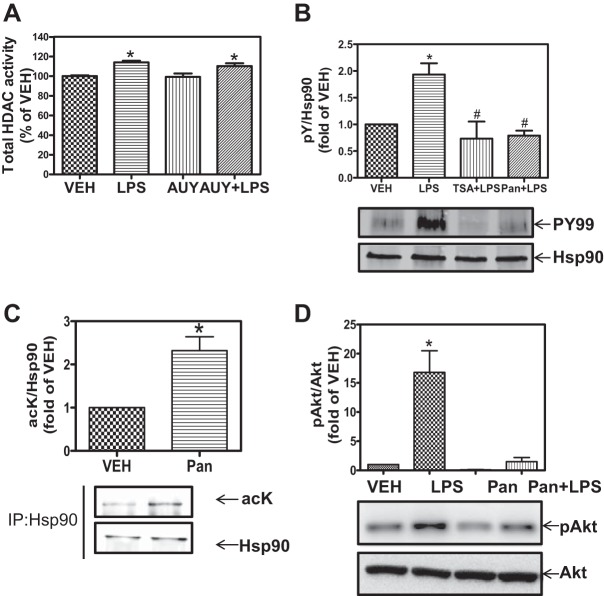
Fig. 2.
HDAC inhibition attenuates LPS-induced heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) chaperone function. A: confluent monolayers were treated with vehicle or 2 μM AUY-922 (Hsp90 inhibitor) for 4 h followed by exposure to LPS (1 EU/ml) for 2 h. Cells were then lysed, and HDAC activity was measured using the Flour-de-lys HDAC activity assay. *P < 0.05 from vehicle or AUY. B: confluent monolayers were treated with vehicle, LPS (1 EU/ml), 1 μM TSA for 2 h followed by exposure to LPS for 2 h, or 1 μM Pan for 2 h followed by exposure to LPS for 2 h. Cells were lysed, and Hsp90 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted for phoshotyrosine and Hsp90. P < 0.05 from vehicle (*) and LPS (#); n = 3. C: HLMVEC were treated with vehicle (VEH) or 1 μM Pan; cells were then lysed, and Hsp90 was immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted for acetyl-lysine and Hsp90. *P < 0.05; n = 3. D: HLMVEC were treated with vehicle, LPS (1 EU/ml), 1 μM panobinostat, or 1 μM panobinostat for 2 h followed by exposure to LPS (1 EU/ml) for 2 h. Cells were then lysed and immunoblotted for phosho-protein kinase B (Akt, S473) and Akt. Densitometric analysis was carried out, and the ratio of pAkt to Akt was plotted. *P < 0.01 vs. vehicle.