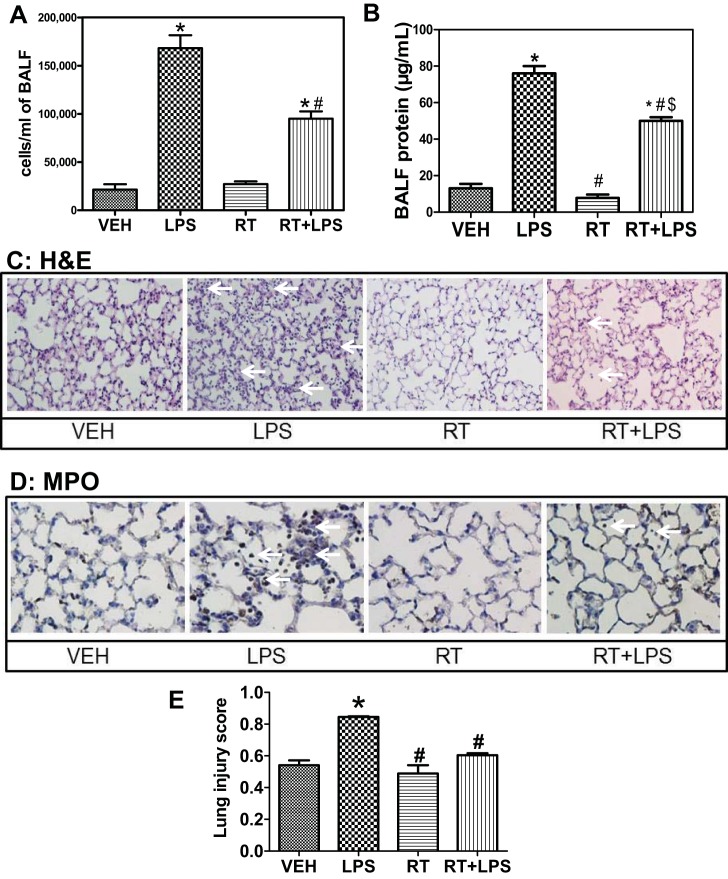
Fig. 8.
Combined pharmacological inhibition of HDAC3 and -6 protects against LPS-mediated acute lung injury (ALI). Mice were injected ip with 10 mg/kg each of RGFP-966 and tubastatin. After 24 h, 1.5 mg/kg LPS were given it, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was collected 24 h later. A: cellular infiltration into the alveolar spaces was quantified by counting the no. of cells in BALF. P < 0.05 from vehicle (*) and LPS (#); n = 7. B: capillary permeability was estimated by measuring protein concentration in BALF using the bicinchonic acid method. P < 0.05 from vehicle (*), LPS (#), and RT ($); n = 7. Histological evaluation of lung samples from treated mice was also performed. C and D: sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (C) or immunocytostained against the granulocyte marker myeloperoxidase (MPO, D). Arrows point to thickened septa and cellular infiltrates. Representative samples of 3 specimens/group. E: estimation of lung injury index as described previously (42). P < 0.05 from vehicle (*) and LPS (#); n = 4.