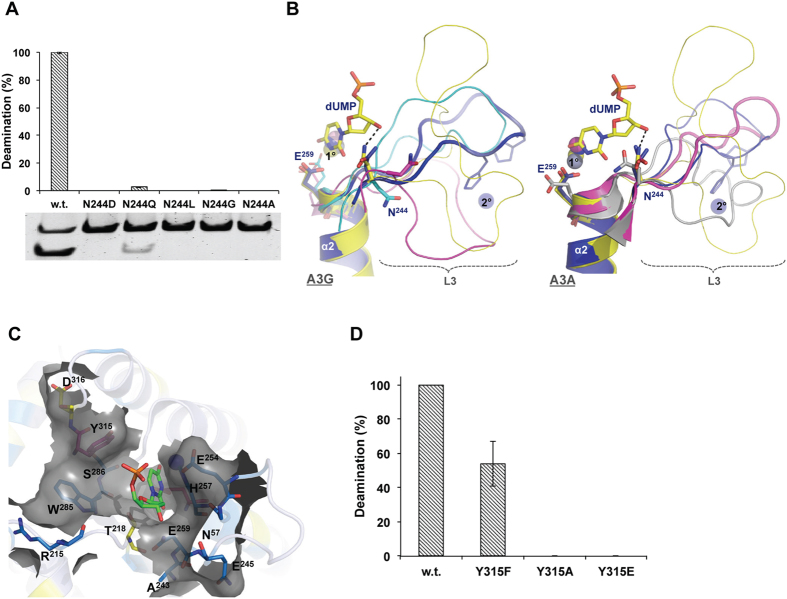
Figure 3. Asn244 is essential for A3GCTD activity.
(A) Relative deamination activity of A3GCTD w.t. and N244 mutants. Error bars represent 3 biological repeats and a representative gel resolving non-deaminated “ND” and deaminated “D” substrate is shown. (B) Structural alignment of A3GCTD (left) and A3A (right). A3GCTD bound (blue: 3IR2) or unbound (magenta: 2JYW, cyan: 2KEM) to a 2° Zn. Shown in yellow is a dCMP deaminase (4P9C) bound to dUMP ligand. A3A monomeric (gray: 2M65) and dimeric (magenta: 4XXO) structures are compared. Shown in blue and yellow are the A3GCTD and dCMP deaminase, respectively. The conserved N244 and E259 are shown in sticks. Catalytic (1°) and 2° zinc ions are shown as spheres. Black dashed line depicts hydrogen bonding between N43 and the dUMP ligand. (C) A3G residues most affected by zinc titration (blue/yellow residues in16) are presented in sticks and gray-surface. dUMP in sticks to depict substrate binding site. Y315 and catalytic E259 in magenta sticks. (D) Relative deamination activity of A3GCTD w.t. and Y315 mutants. Error bars represent 3 biological repeats.