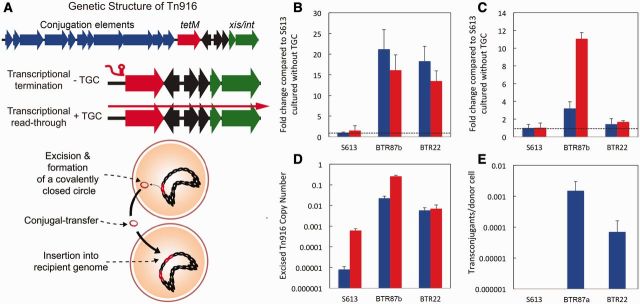
Fig. 2.
Deletions upstream of tetM increase tetM expression and Tn916 conjugation. (A) A diagram outlining the mechanism of Tn916 movement and conjugation. In S613, tetM expression is repressed in the absence of antibiotic by a transcription termination mechanism (indicated as the red hairpin) that is relieved when antibiotic is present. In the presence of antibiotic, leaky transcription through tetM leads to expression of the downstream excisionase (xis) and integrase (int) genes. Upon excision from the genome, Tn916 forms a circular intermediate that coordinates excision events with expression of the genes required for conjugation. (B) Using qPCR, we measured the expression of tetM in S613 and two end-point strains, BTR87b (87-bp deletion in the 5′-UTR of tetM) and BTR22 (22-bp deletion in the 5′-UTR of tetM). The relative expression of tetM in both BTR strains was increased by more than 10-fold over S613 in both the presence (red) and absence (blue) of TGC. (C) As transcriptional read-through of tetM is leaky, we also measured the relative expression of the downstream int gene. The expression of int in the absence of TGC was elevated for both BTR87b (3-fold) and BTR22 (1.5-fold) compared with S613. The expression of int was also elevated in the presence of TGC for BTR87b (11-fold) and BTR22 (1.6-fold). (D) Using qPCR and primers that amplify the new junction associated with excised and circularized Tn916. The number of cells with excised Tn916 increases from approximately 1 in 120,000 cells for S613 to about 1 in 150 cells for BTR22 and over 1 in 4 cells for BTR87b cultured with TGC. Error bars for all qPCR data show the 95% confidence interval between three biological replicates. (E) Conjugation assays were performed in triplicate using E. faecalis OG1RF as a recipient and S613, BTR87a, and BTR22 as donors. No conjugation was detected when S613 was used as a donor, whereas BTR87a and BTR22 produced conjugation frequencies of 1.5 × 10−3 and 7.0 × 10−5 transconjugants per donor cells, respectively.