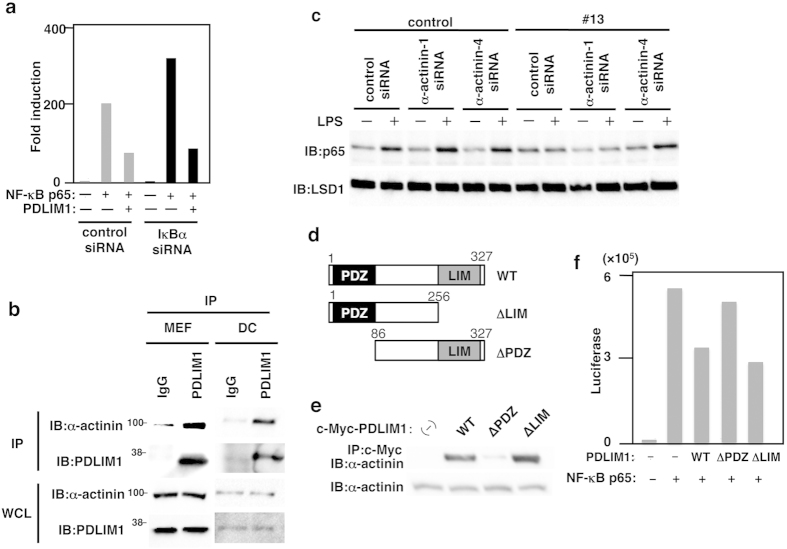
Figure 5. PDLIM1 sequesters p65 in the cytoplasm via association with α-actinin-4.
(a) Luciferase activity in 293T cells transfected first with control siRNA or IκBα-specific siRNA, then transfected with the ELAM-1-luciferase reporter construct along with expression plasmids encoding p65 with or without PDLIM1. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (b) Endogenous interaction between PDLIM1 and α-actinin in MEF (left) and DC (right). Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-PDLIM1 and immunoblotted with anti-α-actinin or anti-PDLIM1 antibody. Western blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. (c) Nuclear extracts in control NIH3T3 cells and NIH3T3 cells expressing PDLIM1, transfected with control, α-actinin-1-specific or α-actinin-4-specific siRNA and left untreated or treated with LPS for 1 hr, analyzed by immunoblot with the indicated antibodies (IB, left margin). Western blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. (d) Depiction of wild-type PDLIM1 (WT) and PDLIM1 mutants lacking the PDZ domain (∆PDZ) or LIM domain (∆LIM). (e) Identification of the domain of PDLIM1 that is required for its association with α-actinin. Whole cell lysates in 293T cells transfected with wild-type or mutants PDLIM1 were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-Myc and immunoblotted with anti-α-actinin antibody. Western blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. (f) Effects of PDLIM1 mutants on p65-mediated gene activation in 293T cells transfected with the ELAM-1-luciferase reporter construct plus expression plasmids encoding p65 and wild-type or PDLIM1 mutants, assessed by measurement of luciferase activity. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.