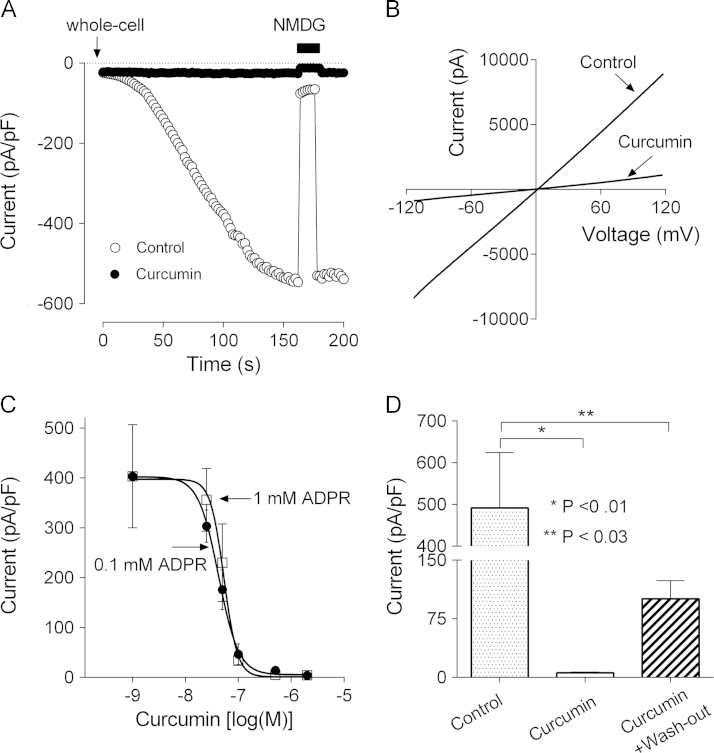
Fig. 4.
Curcumin inhibits ADPR-mediated activation of TRPM2 channels heterologously expressed in HEK 293T cells. (A) Activation of TRPM2 current by 1 mM intracellular ADPR in TRPM2-transfected HEK 293T cells in normal bath solution (control), and after treatment with 5 µM curcumin for 15 min (curcumin). Current was recorded in response to 100 ms voltage ramps between −120 and 120 mV, applied every two seconds. Average current amplitude at −100 mV is plotted against time (n=6 for each condition). (B) Current–voltage plots of ADPR-activated current in TRPM2-transfected HEK 293T cells in normal bath solution (control) and cells treated with 5 µM curcumin for 15 min (curcumin). (C) The dose-response relations of curcumin inhibition of TRPM2 current in transfected HEK 293T cells at two different concentrations of ADPR in the patch pipette (0.1 and 1 mM). The amplitude of ADPR-activated current at −100 mV is plotted against curcumin concentrations (n=5 for each condition). The experimental data points are fitted with Hill equation with variable slope. The IC50 of curcumin block of ADPR-activated current were 42±17 nM and 53±16 nM for 0.1 and 1 mM ADPR, respectively. The Hill slope was 2.3 and 3.3 for 0.1 and 1 mM ADPR, respectively. (D) The wash-out the effect of curcumin on ADPR-activated current in TRPM2-expressing HEK 293T cells. The average amplitude of TRPM2 current measured at −100 mV in cells incubated in the normal bath solution (control), incubated with 2 µM curcumin for 15 min (curcumin), and incubated with 2 µM curcumin for 15-min and then washed out for 10 min (curcumin wash-out).