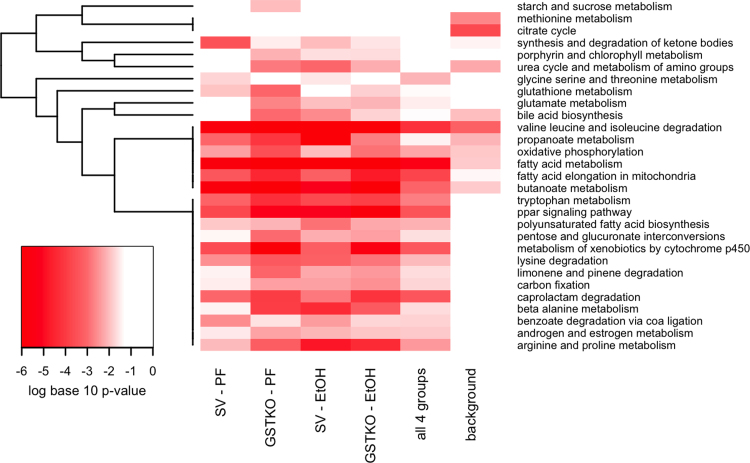
Fig. 4.
KEGG Pathway Bioinformatic analysis of mitochondrial proteins. For enrichment analysis, six groups of proteins were identified and enrichment of pathways for each group are represented in each column. The SV-PF column represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in at least 50% of the pair-fed 129 mice, but not in the background sample. The GSTKO-PF column represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in at least 50% of the pair-fed GSTA4−/− mice, but not in the background sample. The SV-EtOH column represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in at least 50% of the ethanol-fed 129 mice, but not in the background sample. The GSTKO-EtOH column represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in at least 50% of the ethanol-fed GSTA4−/− mice, but not in the background sample. The column labeled ‘all 4 groups’ represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in at least 50% of samples in each of the four groups (PF/EtOH SV/GSTA4−/−), but not in the background sample. The background column represents pathways enriched for proteins identified in the background sample. Proteins functionally annotated using KEGG pathways [23] were examined for enrichment using EnrichR [24]. KEGG pathways that were nominally significant (p<0.01) in at least one of the 6 protein lists are included in the graphic. The colors of the heatmap range from white (unadjusted p-Value>0.05) to bright red based on the log base 10 transformation of the unadjusted p-value. A p-Value of 1 was used when the KEGG pathway was not represented by any proteins in the list. KEGG pathways (rows) are ordered based on hierarchical clustering using the Euclidean distance and a binary indicator of significance (p<0.05 vs. p>=0.05).