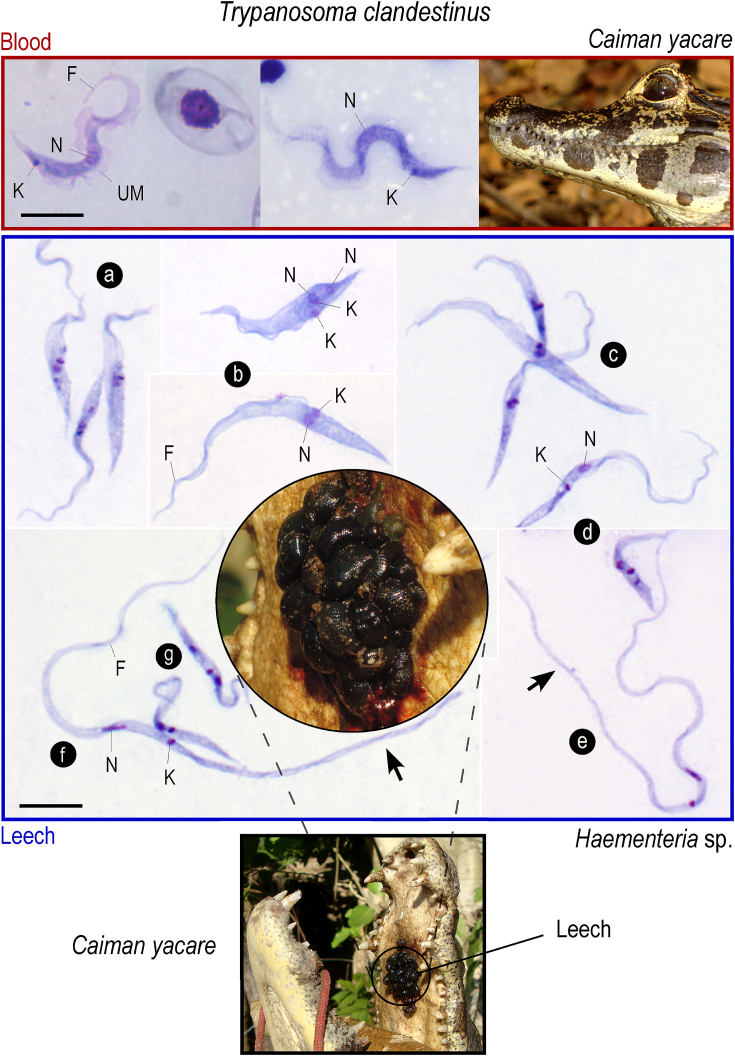
Fig. 3.
Proposed life cycle of T. clandestinus and its developmental and morphological features in caiman blood and leeches. Giemsa-stained blood smears showed blood trypomastigotes of experimentally-infected Caiman yacare, and epi- and trypomastigotes found in the gut of one leech of the genus Haementeria sp. collected in the mouth of a wild Cayman yacare captured in the Pantanal wetland of Brazil. The caiman and the leech trypanosomes were molecularly identified as T. clandestinus. (a–c) epimastigotes; (b) epimastigote dividing by binary fission; (d, g) short trypomastigote; (e,f) long and thin trypomastigotes. Arrow points to the long and thin posterior extremity of very long and slender trypomastigotes. K, kinetoplast; N, nucleus; F, flagellum.