Figure 2. CLPP substrate-trapping assay using isolated mitochondria.
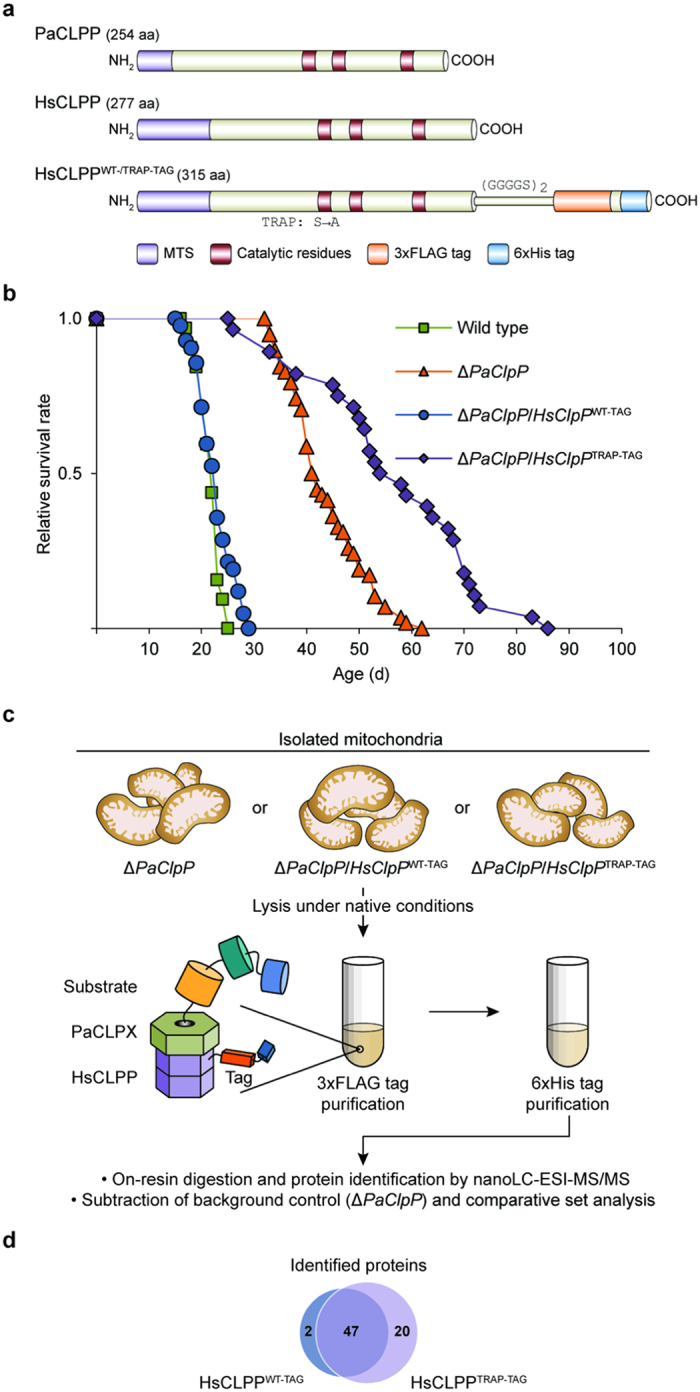
(a) Cartoon presentation of P. anserina and human CLPP homologues as well as recombinant HsCLPP variants. PaCLPP is 254 amino acids and HsCLPP 277 amino acids long. Both CLPP homologues display a conserved distribution of the canonical catalytic residues Ser, His, and Asp and contain a N-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS). Recombinant human CLPP with a C-terminal (GGGGS)2 linker followed by a 3xFLAG-6xHis-tag has a length of 315 amino acids. Catalytic inactivation of recombinant HsCLPP was achieved by mutating its catalytic serine at position 153 of the full-length HsCLPP pre-protein to alanine. (b) Lifespan of wild type (21.8 ± 0.4; n = 32), ΔPaClpP (43.7 ± 1.0; n = 58; P = 8.3E-25), ΔPaClpP/HsClpPWT-TAG (22.7 ± 0.5; n = 42; P = 3.7E-01), and ΔPaClpP/HsClpPTRAP-TAG (56.9 ± 2.9; n = 28; P = 1.9E-17) isolates at 27 °C. Data given in parentheses are mean lifespan ± s.e.m. in days. P-values were determined in comparison to the wild-type sample by two-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test. (c) Overview of CLPP substrate-trapping assay and proteomics work flow. (d) Venn diagram displaying overlap of identified proteins co-purifying with 3xFLAG-6xHis-tagged active (HsCLPPWT-TAG) or inactive human CLPP (HSCLPPTRAP-TAG).
