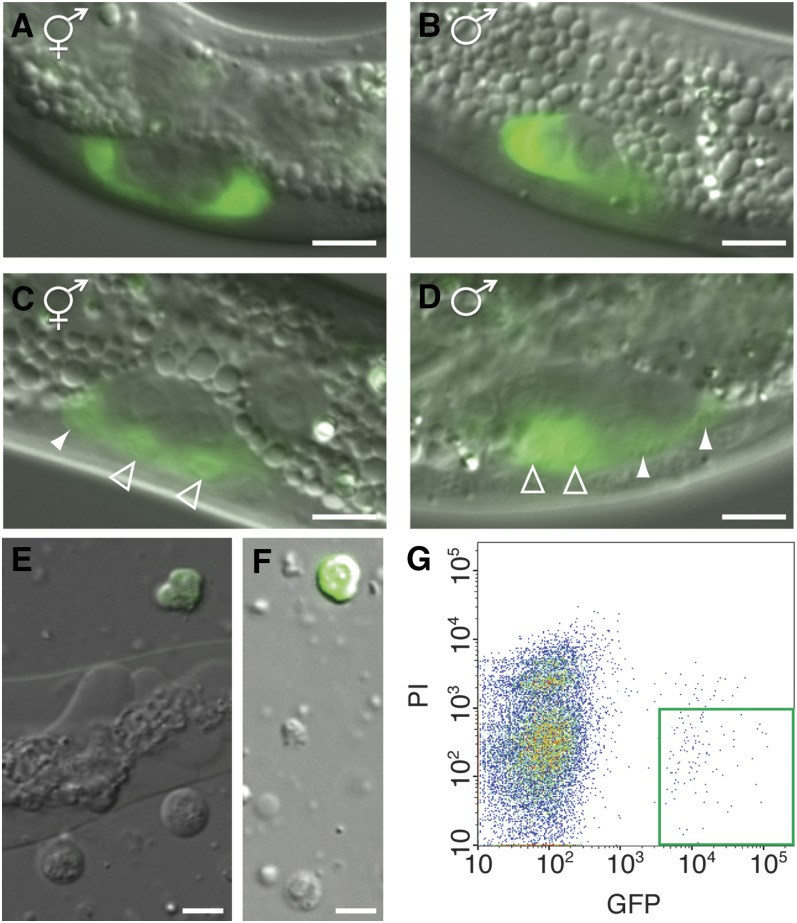
Figure 2.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression in somatic gonadal precursor cells. Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence micrographs of (A) gonad of a hermaphrodite larva at 9.5 hr postfeeding. (B) Gonad of a male larva at 9.5 hr postfeeding. Only Z1 is visible in the male, because Z4 lies outside focal plane. Prior to the division of Z1/Z4 the gonad appears identical between the sexes. (C) Gonad of a hermaphrodite larva at 15 hr postfeeding after the division of Z1/Z4. Distal daughters are marked by filled arrowheads and proximal daughters are marked by open arrowheads. (D) Gonad of a male larva at 15 hr postfeeding after Z1/Z4 daughters have migrated and gonads become sexually dimorphic. Note that distal daughters of Z1/Z4 are smaller. (E) Cell suspension after dissociation. To obtain a large population of healthy dissociated cells, dissociation was stopped while a portion of whole animals were still undissociated. (F) A population of single cells generated by filtering dissociated sample. Scale bar is 5 μm. (G) Density plot shows clear separation by FACS of GFP positive and PI negative Z1/Z4 daughters, which are outlined by the green box.