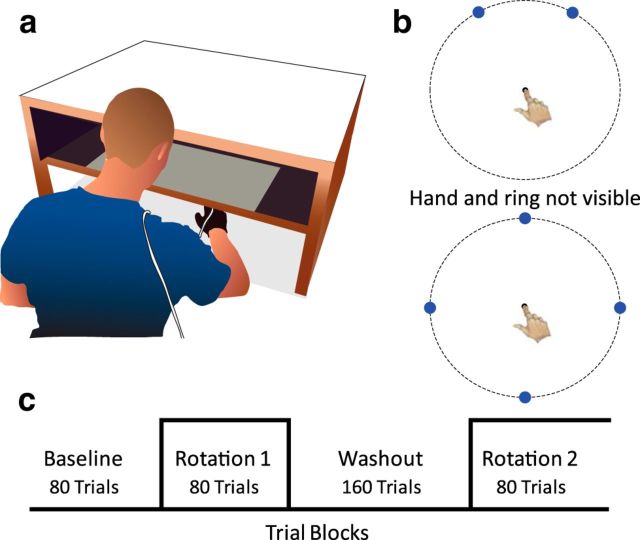
Figure 1.
Experimental task. a, Each participant slid his hand across a tabletop to hit visual targets. Vision of the hand was occluded by a mirror, which reflected a back-projected visual image to create the illusion that the hand and visual targets were coplanar. b, Two- (top) and four- (bottom) target sets used in experiments. On each trial, one target was pseudorandomly selected. The participant reached from a central start location, attempting to “slice” through the target with the cursor. A trial was complete when the radial distance of the movement exceeded 10 cm, indicated here by a dotted ring. c, Task design in Experiment 1 to assess savings. Veridical feedback was provided in the baseline and washout blocks. The visual feedback was perturbed during the two rotation blocks, with the size of the perturbation the same in each of these blocks.