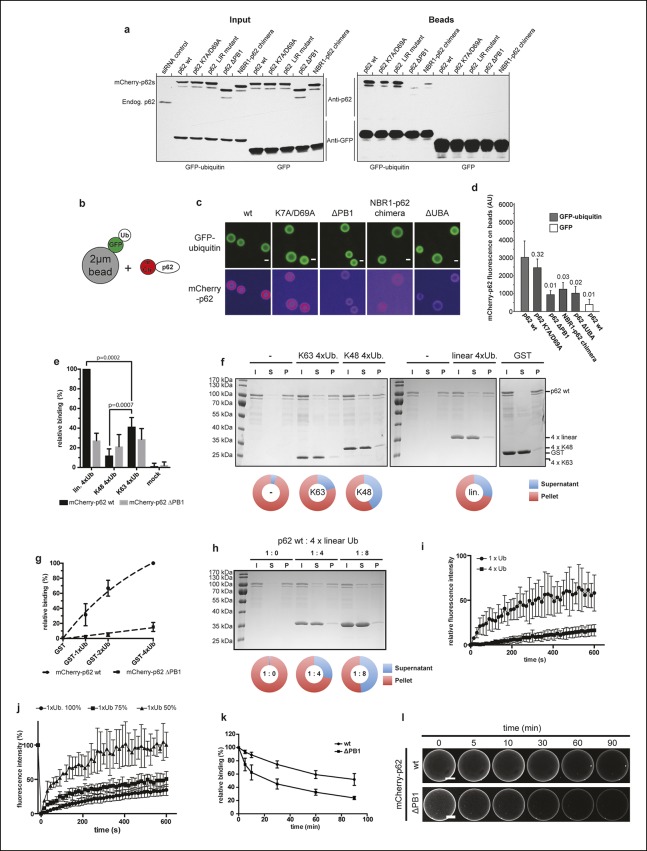
Figure 4. Oligomerization of p62 promotes ubiquitin binding. .
(A) GFP-TRAP experiment using HeLa cell lysates co-expressing GFP (control) or GFP-ubiquitin and the indicated mCherry-p62 variants. The endogenous p62 was silenced by siRNA treatment. Eight percent input and 100% of the bead fractions were analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP and anti-p62 antibodies. (B) Scheme of the set-up of the experiment shown in (C) and (D) Recombinant GFP-ubiquitin was cross-linked to 2 µm latex beads and incubated with purified mCherry-p62 variants at 50 nM final concentration. Beads were observed using a spinning disk microscope under steady-state conditions. (C) Representative images of the recruitment of mCherry-p62 variants on GFP-ubiquitin-coated beads. Pictures were taken using the same microscopy settings and shown in false color for the mCherry-p62 signal (ImageJ: fire). Scale bar 1 μm. (D) Quantification of mCherry-p62 recruitment to beads coated with GFP-ubiquitin or GFP. Averages and SD of three independent replicates are shown. Indicated p-values were calculated with a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (E) Quantification of steady-state binding of the indicated p62 variants to the indicated ubiquitin chains cross-linked to 2 µm latex beads. Averages and SD of three independent replicates are shown. All data are normalized to wild-type mCherry-p62 binding to linear tetra-ubiquitin. p-Values were calculated using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.(F) Coomassie-stained gels showing p62 sedimentation assays conducted with recombinant wild-type mCherry-p62 in the presence of the indicated tetra-ubiquitin chains. GST was used as a negative control. For each sample, the input, supernatant, and pellet fractions are shown. Quantifications are shown below the gel. The protein amount in the pellets and supernatants are expressed as fractions of the input. (G) Quantification of steady-state binding of the indicated p62 variants to beads coated with GST-mono-, di- or –tetra-ubiquitin. GST was used as negative control. Averages and SD of at least three independent experiments are shown. Data are normalized to wild-type mCherry-p62 binding to GST-tetra-ubiquitin. Data points were fitted to mono-exponential curves (dashed lines). (H) p62 co-sedimentation assay with increasing concentrations of linear tetra-ubiquitin. Wild-type mCherry-p62 was incubated with linear tetra-ubiquitin chains at the indicated molar ratios before ultracentrifugation. Inputs, supernatants and pellets were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining. Quantification was performed as described for (F). (I) Fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching (FRAP) curves of wild-type mCherry-p62 recruited to mono-ubiquitin or tetra-ubiquitin-coated beads. Averages and SD of six independent FRAP recordings are shown. (J) FRAP curves of wild-type mCherry-p62 recruited to beads coated with decreasing concentrations of mono-ubiquitin. For each sample, the averages and SD from six independent FRAP recordings are shown. (K) Quantification of wild-type and delta PB1 mCherry-p62 decay from GST-di-ubiquitin-coated beads. Averages and SD of three independent replicates are shown. (L) Representative images of data shown in (K). For better comparison, brightness was adjusted so that intensities of beads at time 0 is identical. Scale bars, 25 μm. (D) Total beads counted per condition: GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-p62 wild-type = 565; GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-p62 K7A/D69A = 383; GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-p62 delta PB1 = 378; GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-NBR1-p62 chimera = 476; GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-p62 LIR mutant = 393; GFP-ub coated beads + mCherry-p62 ∆UBA = 347; GFP coated beads + mCherry-p62 wild-type = 187.(E) Total beads quantified per condition: mCherry-p62 WT: M1 4xUB = 427; K48 4xUB = 332; K63 4xUB = 305; mock = 95. mCherry-p62 delta PB1: M1 4xUB = 266; K48 4xUB = 239; K63 4xUB = 226; mock = 75.(G) Total beads quantified per condition: mCherry-p62 wild-type: GST = 107; GST-mono-ubiquitin = 182; GST-di-ubiquitin = 149; GST-tetra-ubiquitin = 236. mCherry-p62 delta PB1) GST = 113; GST-mono-ubiquitin = 165; GST-di-ubiquitin = 134; GST-tetra-ubiquitin = 241. (K) Total beads quantified: wild-type = 83, delta PB1 = 65.