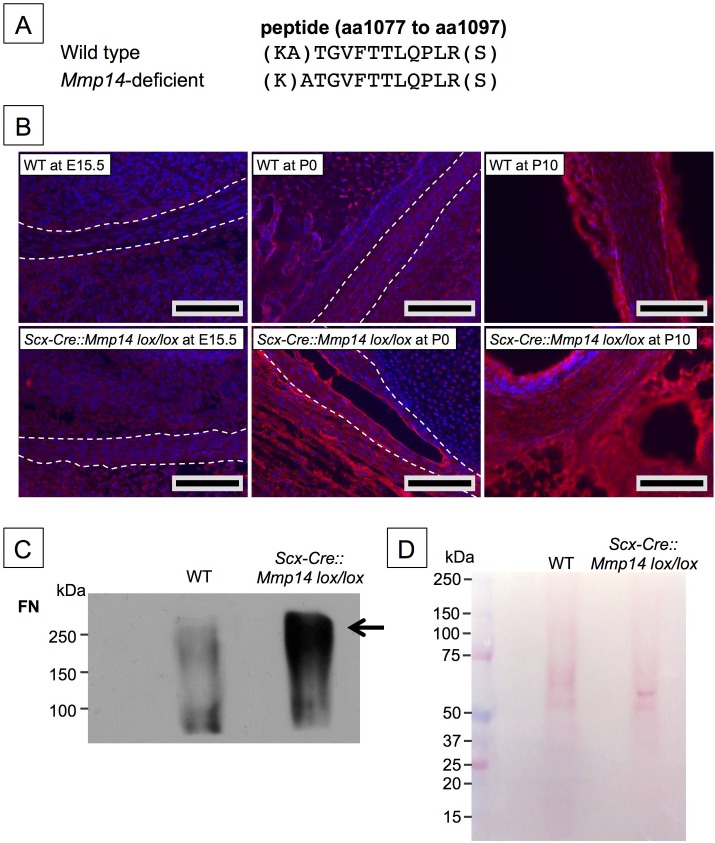
Figure 6. Elevated FN in Mmp14-deficient tendons.
(A) Sequence of a unique semi-tryptic peptide of FN identified in neonatal (P7-10) WT tendon and the sequence of the corresponding peptide from Mmp14-deficient tendons without the additional Ala(1078)-Thr(1079) cleavage. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of FN in tendons of WT and Scx-Cre::Mmp14 lox/lox mice at E15.5, P0, and P10 of development. Scale bars 200 µm. (C) Western blot analysis of P7 WT and Scx-Cre::Mmp14 lox/lox tendons show elevated FN in Mmp14-deficient tendons. (D) Ponceau S-stained membrane shows equivalent extractability of WT and Scx-Cre::Mmp14 lox/lox tendons.