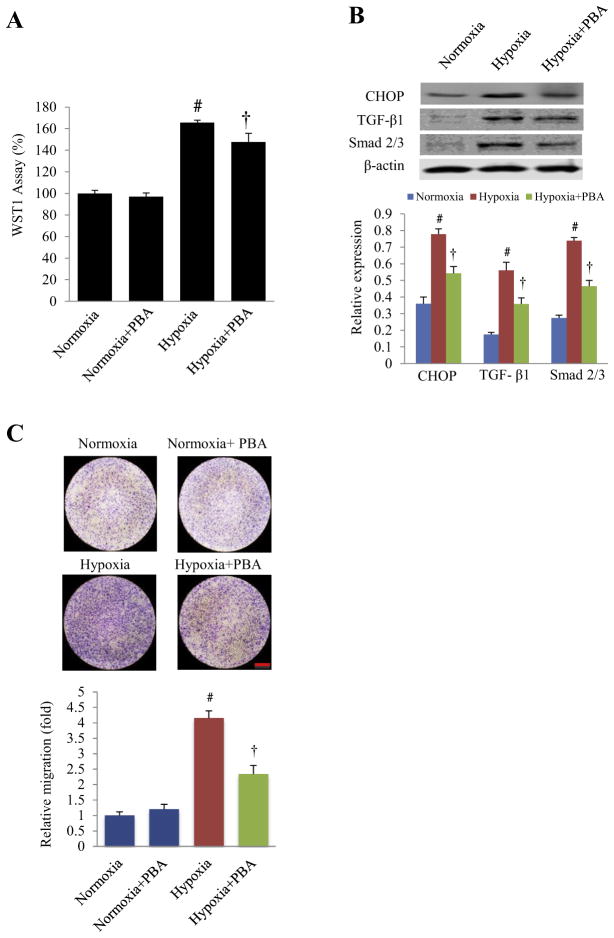
Fig. 4.
Effects of 4-PBA treatment on proliferation and migration of cultured neonatal rat cardiac fibroblast under hypoxia. (A) After 72 h of hypoxia (3% oxygen), the viability of neonatal rat cardiac fibroblasts was measured by the WST1 assay with or without 4-PBA treatment. #P < 0.01 vs. normoxia; †P < 0.01 vs. hypoxia; n = 15 (plate holes). (B) Representative Western blots and quantitative analysis of CHOP, TGF-β1 and Smad 2/3 in the cultured cardiac fibroblasts under hypoxia for 72 h. #P < 0.05 vs. normoxia; †P < 0.05 vs. hypoxia; n = 5. (C) Cell migration was detected by transwell migration assay. After 72 h of hypoxia with or without 4-PBA, fibroblasts in the inner membrane of transwell chamber were wiped away. After the transwell membranes were dry, the opposite side of the membrane was stained by crystal violet to detect the migrated cells (top) with quantitative analysis of fibroblast migration (bottom). #P < 0.05 vs. normoxia; †P < 0.05 vs. hypoxia; n = 3 in each group. Scale bar, 1 mm.