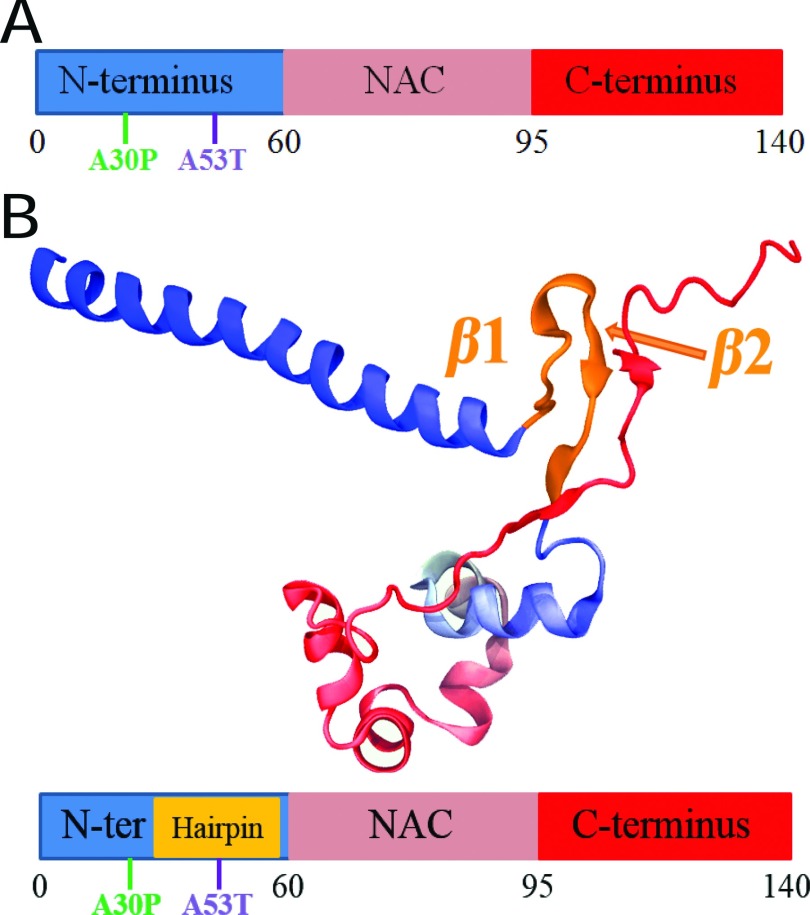
FIG. 1.
Overall structural features of α-synuclein monomer. (a) Schematic depiction of α-synuclein structure. N-terminus, NAC region, and C-terminus are colored blue, pink, and red, respectively. Starting and ending residue ID for N-terminus, NAC region, and C-terminus are labeled. The locations of point mutations, A30P and A53T, are labeled in green and blue, respectively. (b) Representative structure of α-synuclein conformations containing β-hairpins. The representative structure is chosen from the center structure of all sampled α-synuclein conformations with the β-hairpin conformations, such that the backbone of each member of the β-hairpin conformations in the group falls within a RMSD distance of 6 Å to the center structure. N-terminus, NAC region, and C-terminus are colored blue, pink, and red, respectively. Part of the C-terminus forms a β-strand attached to the β-hairpin. The first two regions involved in the fibril core are labeled β1 (region 38-44) and β2 (region 47-53). The coloring scheme used is applied throughout the further figures of this study. Shown beneath the structure is a schematic depiction of the β-hairpin. The coloring scheme is the same as that in panel (a) except for the gold part denoting the β-hairpin region. The schematic depiction serves as a structural guide of α-synuclein in further figures.