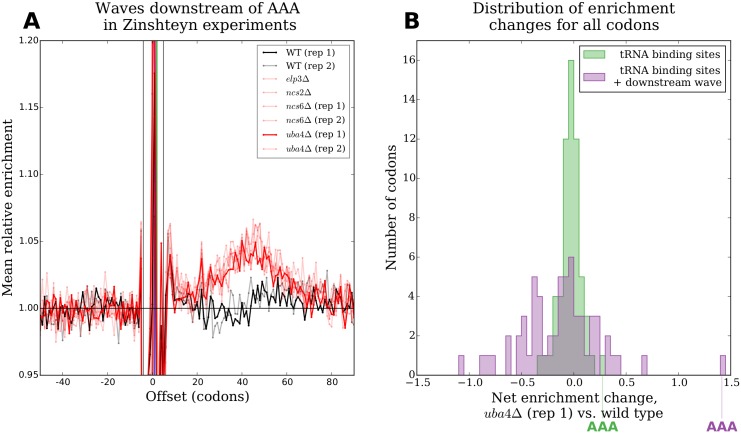
Fig 8. Downstream waves recover the expected effects of lacking tRNA modifications.
(A) Profiles of mean relative enrichments around AAA in two wild type experiments (black lines) and six experiments with different components of the mcm5s2U pathway deleted (red lines) from Zinshteyn [23]. All mcm5s2U deletion strains produce clearly increased waves downstream of AAA compared to wild type. Darker lines correspond to the experiments compared in (B). (B) Histograms of the net change in enrichment for each codon identity between uba4Δ and wild type at the A-, P-, and E-sites (green) or at the A- P, and E-sites plus 7 to 90 codons downstream (purple). AAA shows a modest increase in net enrichment at the tRNA binding sites, but a dramatically larger increase in net enrichment if the area of downstream waves is also taken into account. This suggests that AAA does take substantially longer to decode in vivo in uba4Δ than in wild type, but that most of this difference disappears during continued elongation in the presence of CHX.