Fig 4. Photomicrographs of extraction sockets in SD/control (A-C), SD/ZOL (D-F), SDT/control (G-I), and SDT/ZOL (J-L) rats.
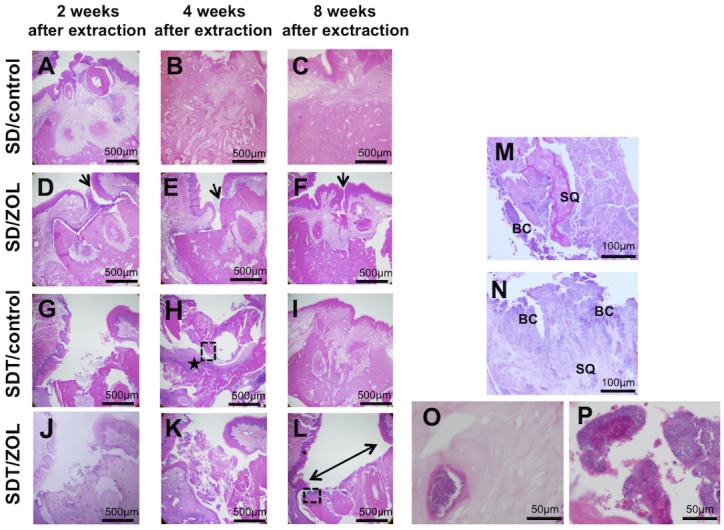
Healed gingival mucosa with complete epithelial coverage in the SD/control group. (D, E) Partial deficiency of epithelial coverage at 2 and 4 weeks in the SD/ZOL group (arrow). (F) Nonkeratinized oral epithelium grew towards the sequestrum at 8 weeks after tooth extraction in 1 of 6 SD/ZOL rats (arrow). (G) Unhealed open socket with an area of exposed bone and no mucosal coverage at 2 weeks after extraction in the SDT/control group. (H) Interstitial tissue (★) under bone sequestra at 4 weeks after extraction. (I) Healed gingival mucosa with complete epithelial coverage at 8 weeks after extraction in the SDT/control group. (J, K) Unhealed open sockets with an area of exposed bone and no mucosal coverage at 2 and 4 weeks after extraction in the SDT/ZOL group. (L) Open sockets without epithelial lining (left right arrow) at 8 weeks after extraction in the SDT/ZOL group. H&E stain, original magnification, ×40. Photomicrographs of magnifying dotted square area in (H) and (L). (M) Necrotic bone sequestra (SQ) with empty osteocyte lacunae covered with bacterial colonies (BC) and marked inflammation in (H) of SDT/control rat. (N) Necrotic bone sequestra (SQ) with empty osteocyte lacunae covered with bacterial colonies (BC) and less inflammation in (L) of SDT/ZOL rat. H&E stain, original magnification, ×200. (O) High magnification of empty osteocyte lacunae and (P) bacterial colonies in SDT/ZOL rats. H&E stain, original magnification, ×400.
