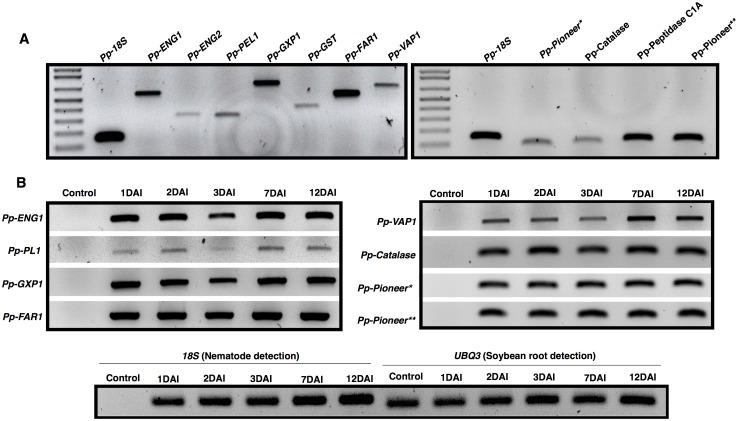
Fig 3. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR showing the transcript levels for a subset of predicted Pratylenchus penetrans transcripts.
(A) RT-PCR amplification was performed using the generated cDNA from total RNA collected from a pool of mixed stages (eggs, juveniles and adult stages) of P. penetrans. (B) Upper panel: detection of a subset of P. penetrans genes putatively involved in parasitism using total RNA extracted from nematode infected soybean roots, at different days after nematode infection (1, 2, 3, 7 and 12 days after infection). Lower panel: the nematode 18S rDNA gene was used as control to validate the presence of P. penetrans in the infected roots, while UBQ3 gene was used to validate plant gene detection. Control corresponds to non-infected soybean roots.