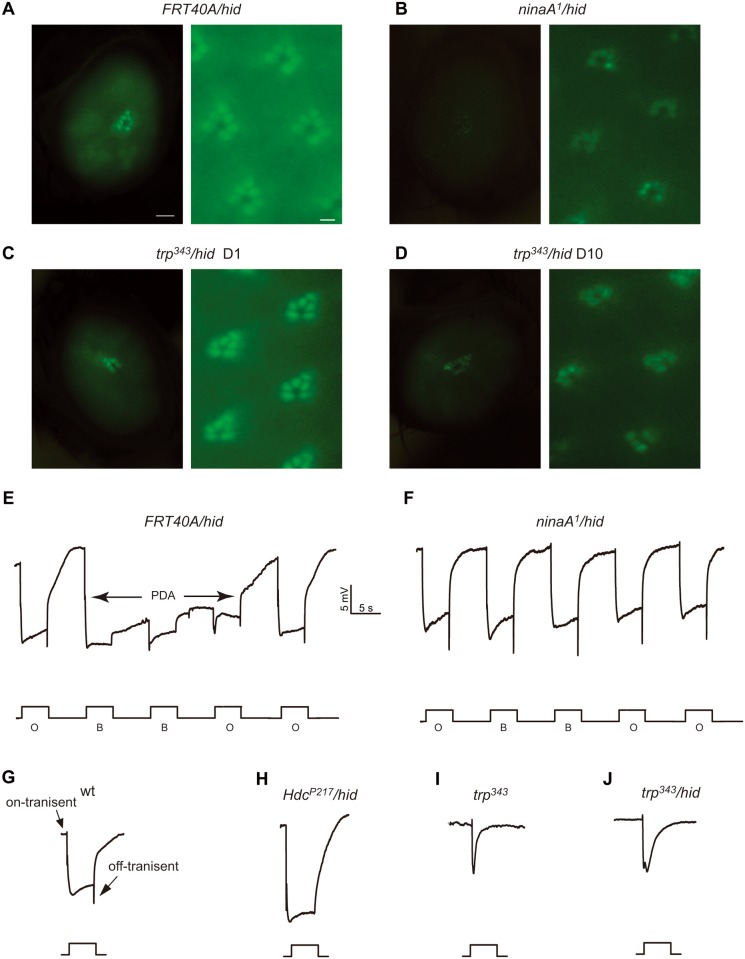
Fig 3. Analysis of mutants of rhodopsin homeostasis, retinal degeneration, and phototransduction with the Rh1::GFP ey-flp/hid method.
(A-E) Detection of fluorescence in the deep pseudopupil (left panels) and by cornea optical neutralization (right panel). (A) FRT40A/hid, (B) ninaA 1 /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP;ninaA 1 FRT40A/GMR-hid CL FRT40A), (C) trp P343 /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP;FRT82B trp P343 / FRT82B GMR-hid CL), (D) trp P343 /hid 10 day-old. 1 day-old flies were used, with the exception of the trp P343 /hid flies, which were 10 day-old (D). Scale bar in right panels, 50 μm; in the left panels, 2μm. (E-H) ERG recordings of (E) wild type and (F) ninaA 1 /hid flies. Flies were exposed to 5 s pulses of orange light (O) or blue light (B), interspersed by 7 s, as indicated. A PDA was induced in the wild-type by blue light and terminated by orange light (arrows). (G-J) ERG response of (G) wild-type, (H) Hdc P217 /hid, (I) trp P343, and (J) trp P343 /hid flies in response to a 5-s orange light stimulus.