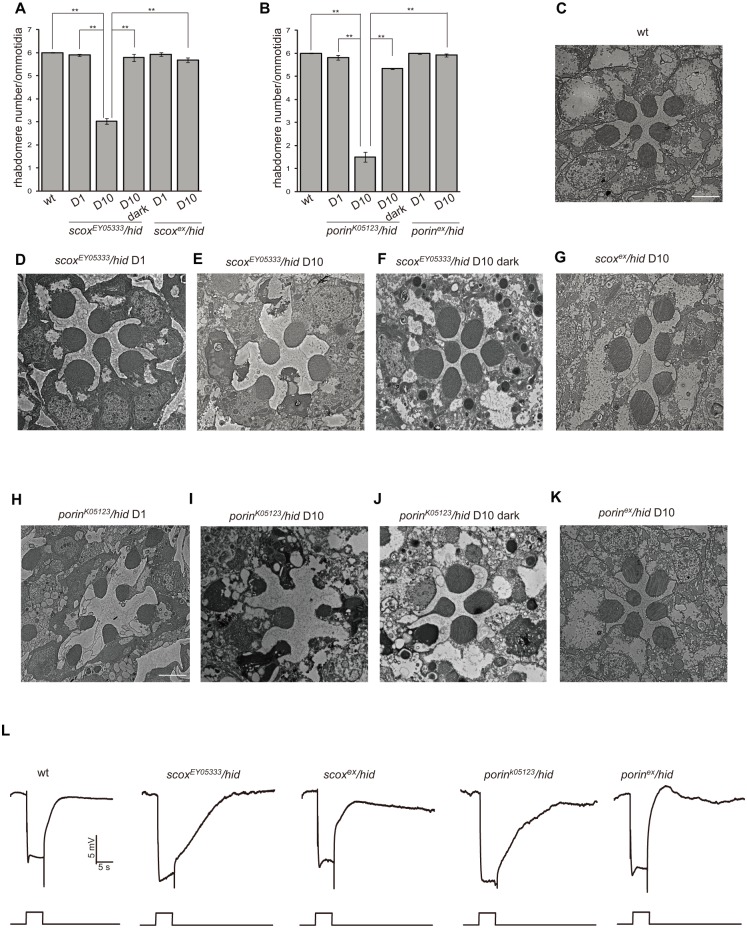
Fig 4. The scox and porin mutations lead to light-dependent photoreceptor cell degeneration.
(A-B) Average rhabdomere numbers per ommatidia of (A) the scox mutant flies and (B) the porin mutant flies under the indicated conditions. Each data point was based on examination of >60 ommatidia from >3 flies. Error bars represent the SD. Asterisks indicate statistically-significant differences (one-way ANOVA and post-hoc Dunnett’s test, **p < 0.01). (C-K) Transmission electron microscopy sections of single ommatidia of fly compound eyes with the indicated genotype and conditions. (C) 10 day-old wild-type, (D) 1 day-old scox EY05333 /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP; scox EY05333 FRT40A/GMR-hid CL FRT40A), (E) 10 day-old scox EY05333 /hid, (F) 10 day-old scox EY05333 /hid under dark condition, (G) 10 day-old P-element excised scox ex /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP; scox ex FRT40A/GMR-hid CL FRT40A), (H) 1 day-old porin k05123 /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP; porin k05123 FRT40A/GMR-hid CL FRT40A), (I) 10 day-old porin k05123 /hid, (J) 10 day-old porin k05123 /hid under dark condition, (K) 10 day-old p-element excised porin ex /hid (ey-flp Rh1::GFP; porin ex FRT40A/GMR-hid CL FRT40A). Scale bar, 2 μm. With the exception of the dark-reared (F) scox EY05333 /hid and (J) porin k05123 /hid flies, flies were maintained under a 12 hr light/12 hr dark cycle. (L) ERG responses of wild-type, scox EY05333 /hid, scox ex /hid, porin k05123 /hid, and p-element excised porin ex /hid flies in response to a 10-s orange light stimulus as indicated. Flies used were less than 2 days old.