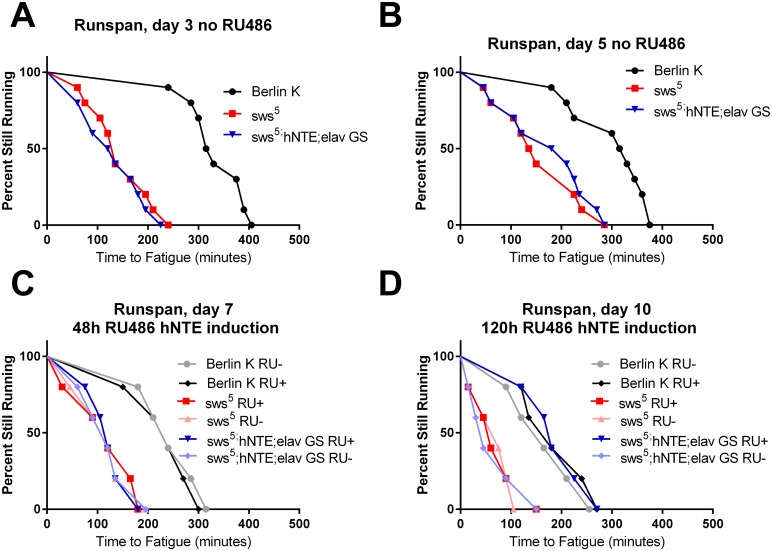
Fig 4. Delayed hNTE expression rescues endurance in sws 5 flies.
Endurance tolerance was assessed before (A, B) and after (C, D) mifepristone (RU486) application and induction of hNTE expression. (A) Berlin K flies exhibit wild-type endurance on day 3 of adulthood, while both sws 5 mutant and sws 5 ;hNTE;elav GS show a marked reduction in time-to-fatigue (n = 200 for all groups, log-rank, p<0.0001). (B) 48 hours later sws 5 mutant and sws 5 ;hNTE;elav GS cohorts continue to exhibit much lower endurance than Berlin K controls (n = 200 for all groups, long-rank, p<0.0001). At the end of the day-5-test, cohorts are divided in half and split into induced (RU+) and control (RU-) groups. (C) The same flies from (A) and (B) are tested for endurance 48 hours after mifepristone induction. Berlin K flies begin to decline in performance compared to day 5, independent of RU486 feeding (log rank, p≤0.0001 for RU+ and RU-). sws 5 mutant and sws 5 ;hNTE;elav GS cohorts show reduced endurance relative to Berlin K whether RU486-fed or not (n = 100 for all groups, long-rank, p<0.0001). (D) On day 10, after 120 hours RU486 induction, hNTE rescue flies’ (sws 5 ;hNTE;elav GS RU+) time-to-fatigue is fully rescued to wild-type Berlin K endurance capacity (log rank, p = 0.9436). sws 5 mutant and RU- control groups remain deficient in time-to-fatigue (log rank, p<0.0001). n = 100 for all cohorts.