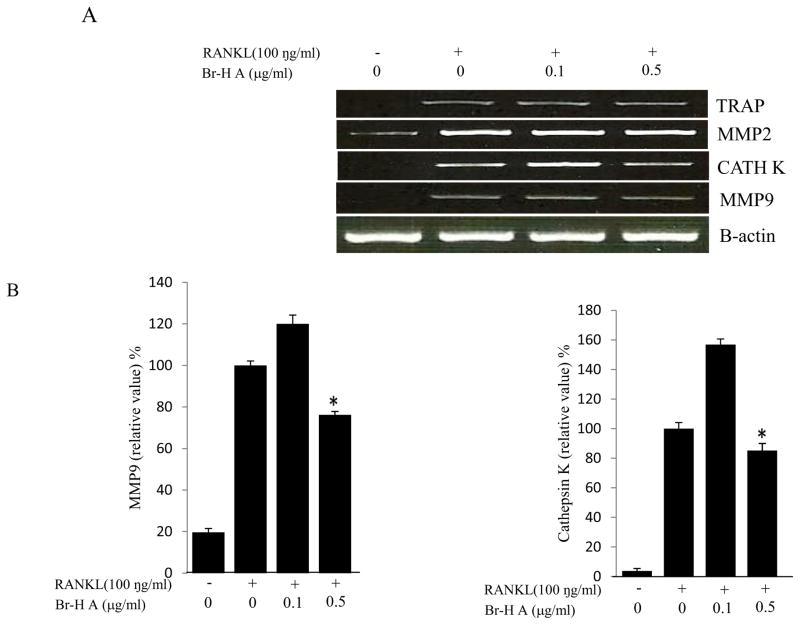
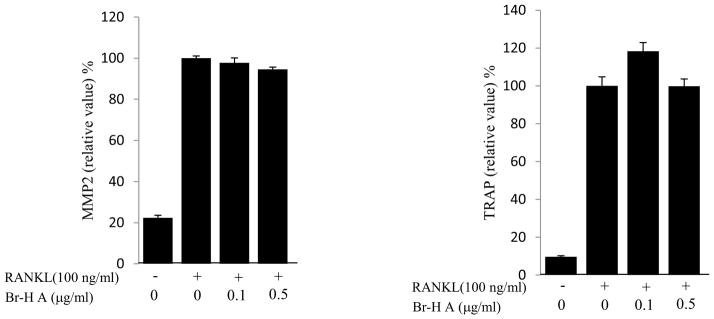
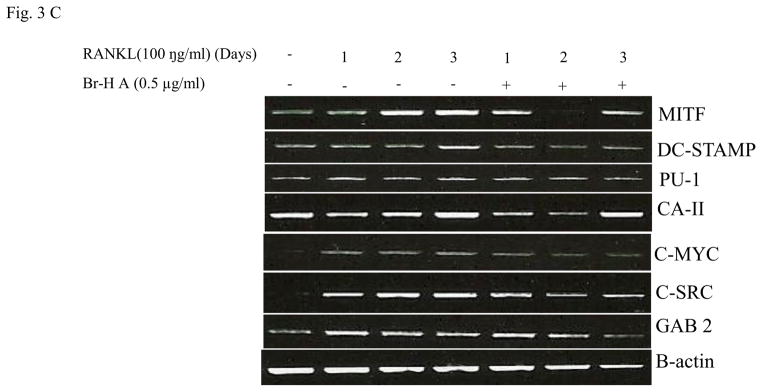
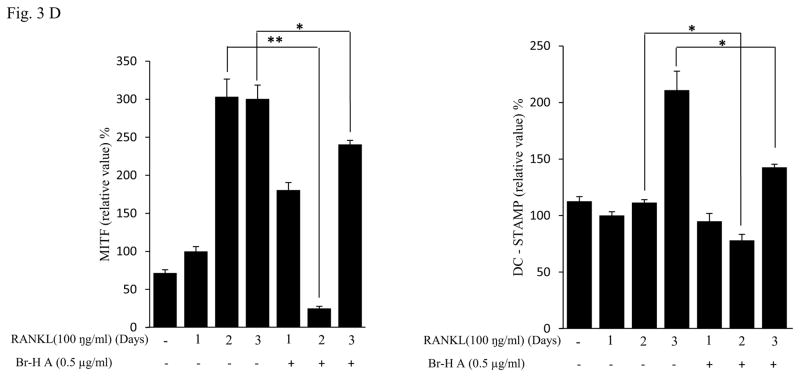
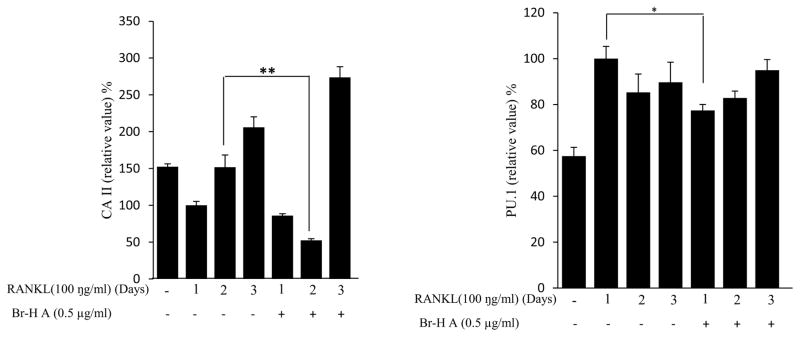
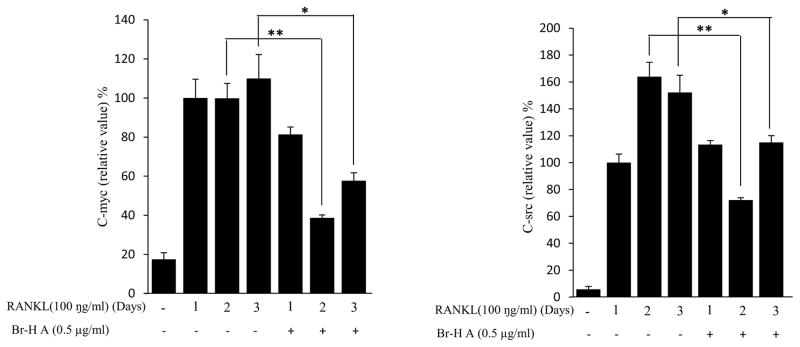
Fig. 3.
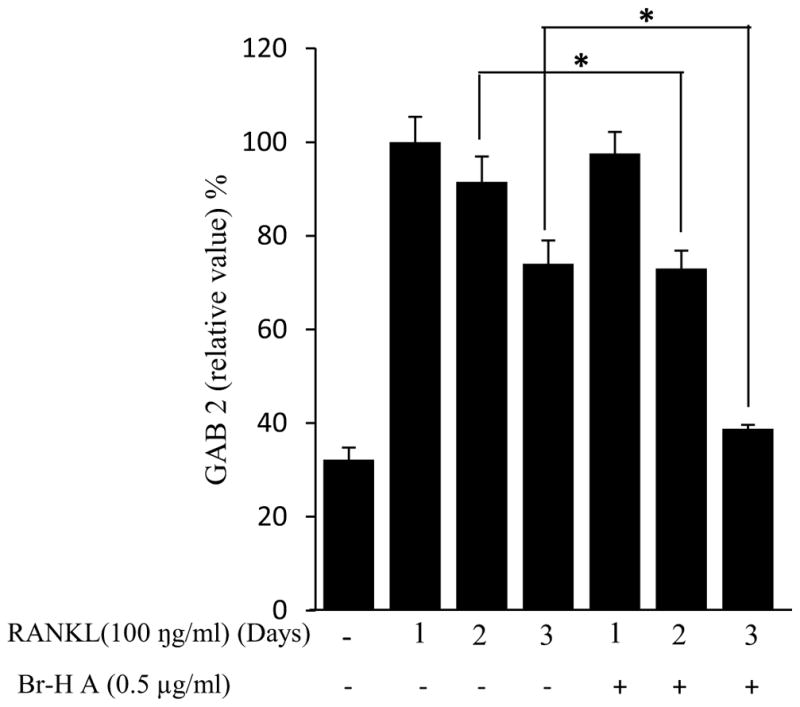
Effect of Br-H A on mRNA expression of osteoclastic marker genes in RANKL stimulated RAW264.7 cells. (A) RAW 264.7 cells (3.0 × 105 cells/mL) were pre-incubated for 16 h, and the cells were stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/mL) in the presence of Br-H A (0.1 and 0.5 μg/ml) for 4 days. The expressions of mRNA osteoclastogenic marker genes were determined using RT-PCR. (B) The histogram represents the levels of the mRNA expression (%) compared with that of the control. Values are expressed as means ± S.D. of triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05 indicates significant differences from the RANKL-stimulated group. (C) RAW264.7 cells (3.0 × 105 cells/ml) were pre-incubated for 16 h, and the cells were stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/ml) in the presence of Br-Honaucin A 0.5 μg/ml for 1, 2, 3 days. mRNA expressions of osteoclastogenic marker genes were determined using RT-PCR. (D) The histogram represents the levels of the mRNA expression (%) compared with that of the control. Values are expressed as means ± S.D. of triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 indicate significant differences from the RANKL-stimulated group.