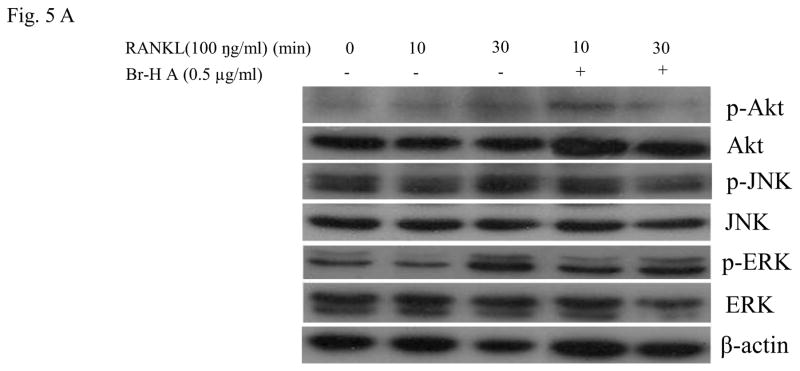
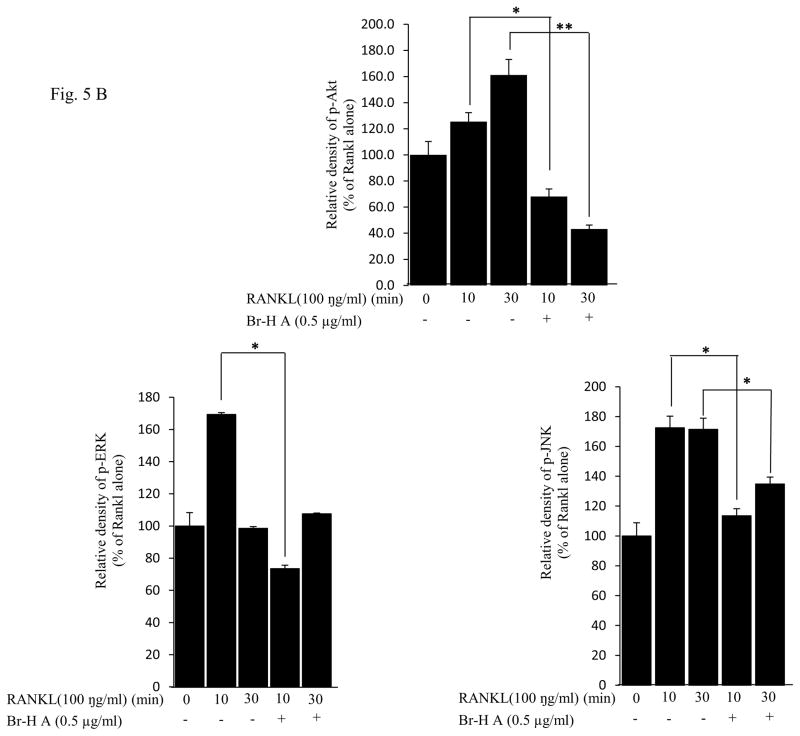
Fig. 5.
Effect on MAPK and Akt. (A) MAPK protein level in RANKL-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells (1.0 × 106 cells/mL) were cultured for 16 h, pre-incubated with 0.5 μg/ml of Br-H A for 30 min, and stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/ml) for the indicated times. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies specifically directed against the phosphorylated forms of the enzymes, compared to data obtained with antibodies directed against the unphosphorylated states of the kinases. Equal amounts of protein were loaded in each lane as calibrated by the level of β-actin. (B) The histogram represents the percent relative density of the MAPK compared with that of the control. Values are expressed as mean ± S.D. of triplicate experiments. *P<0.05 and **P<0.001 indicate significant differences from the RANKL