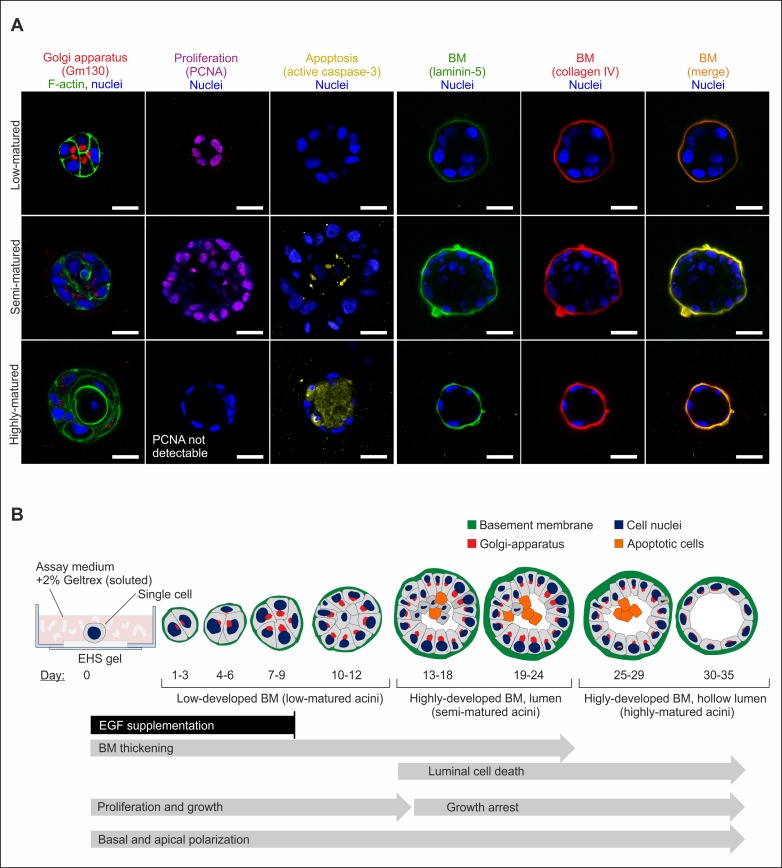
Fig 2. Capturing the differentiation process of MCF10A acini.
A. Equatorial cross sections through MCF10A acini demonstrate the differentiation process leading to apical and basal polarization. Basal polarization markers: laminin-5, collagen IV (BM formation). Apical polarization markers: GM-130 (Golgi apparatus). Proliferating-nuclear-antigen PCNA and active caspase-3 marked s-phase and apoptotic cells, respectively. DRAQ5 was used to counterstain cell nuclei, cytoskeletal F-actin was stained with actin-phalloidin. Note that stains were performed on different spheres for low (1–12 days)-, semi (13–24 days)-, highly (25–35 days)-matured states. Scale bars = 20 μm. B. Immunofluorescence data were used to infer the development of acinar structures depending on temporal EGF withdrawal. Temporal progression is highlighted with arrows. Acini were grouped according to their differential grades.