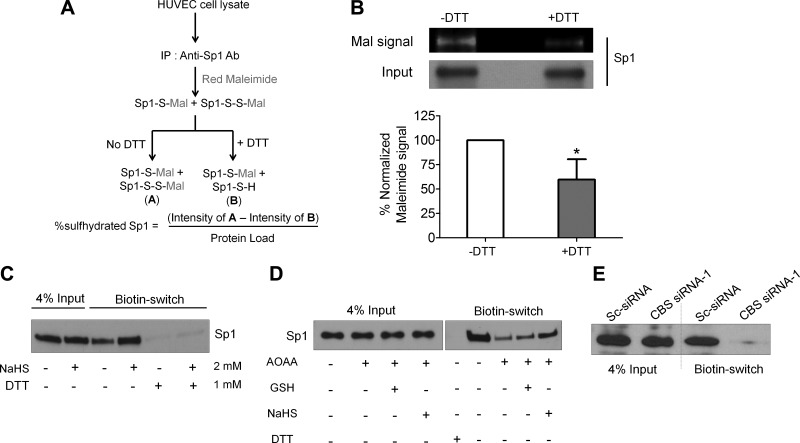
Figure 7.
Sulfhydration of Sp1 augments DNA binding to the VEGFR-2 promoter. A) Schematic representation for detection of sulfhydration of endogenous Sp1 by maleimide assay. B) Maleimide assay to determine the extent of endogenous Sp1 sulhydration in HUVECs. Decrease in red maleimide signal upon DTT treatment establishes sulfhydration of endogenous Sp1. Data represent means ± sd (n = 3), 2-tailed Student’s t test. *P ≤ 0.05. C) Modified biotin switch assay to ascertain sulfhydration of Sp1 in untreated and 2 mM NaHS-treated HUVECs for 6 h. D) Modified biotin-switch assay to determine effect of silencing CBS function with 2 mM AOAA (24 h) on sulfhydration of Sp1and the rescue of Sp1 sulfhydration status with reduced GSH (2 mM) and NaHS (2 mM) treated for 21 h. E) Modified biotin switch assay to ascertain sulfhydration of Sp1 in scrambled control siRNA or CBS siRNA-1-treated HUVECs after 48 h transfection. F) LC-MS/MS analysis of purified full-length Sp1 protein with or without treatment of 100 µM NaHS for 30 min reveals sulfhydration of Cys68 and Cys755. The modified cysteine are labeled red and oxidized methionine are labeled blue.