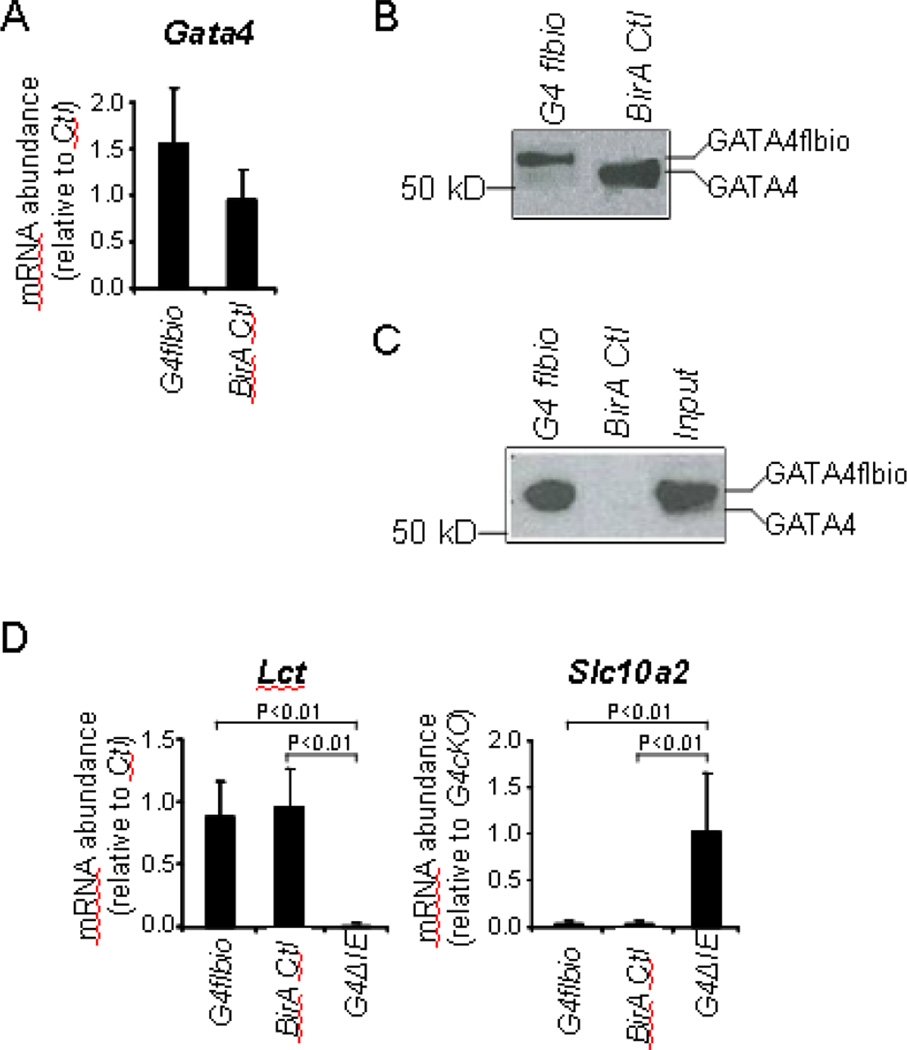
Fig. 1.
GATA4flbio is expressed at near endogenous levels, efficiently biotinylated, and functional in jejunal epithelium of G4flbio mice. (A) Gata4 mRNA abundance, determined by qRT-PCR using mouse Gata4 cDNA primers (mean ± SD, n = 4 in each group), and (B) Western blot analysis using a GATA4 antibody shows that Gata4 is expressed at near endogenous levels in mouse epithelial cells of G4flbio mice as compared to BirA Ctl mice. (C) Streptavidin-biotin pull-down assays showing efficient pull-down of GATA4flbio from nuclear extracts of jejunal epithelium fromG4flbio mice. GATA4flbio was detected by Western analysis using a GATA4 antibody. Input is the extracts isolated from G4flbio mice that have not undergone biotin-streptavidin pull-down, and represents 10% of that used in the pull-down assay. (D) Messenger RNA abundance of the Gata4 target genes, Lct and Slc10a2, in G4flbio mice reveals no difference in gene expression from BirA Ctl mice, demonstrating that GATA4flbio is functional. As a control for impaired GATA4 function, G4ΔIE mice demonstrate the expected down-regulation and up-regulation of Lct and Slc10a2, respectively. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n = 4 in each group.