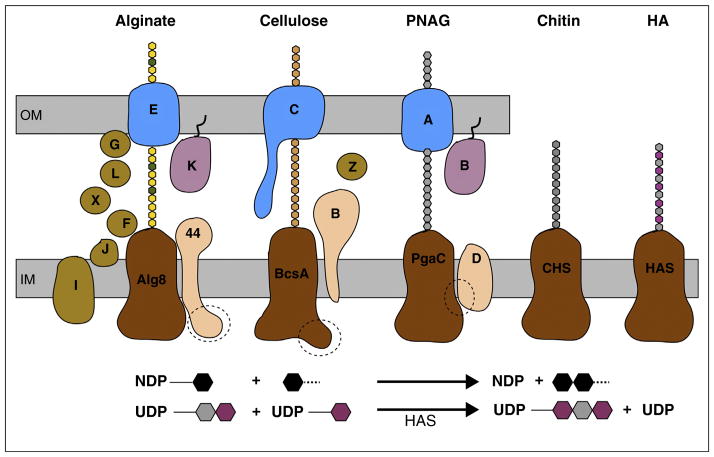
Figure 1.
Membrane-integrated processive GTs synthesize and secrete diverse polysaccharides. The synthases may be part of multi-component complexes or function on their own. The catalytically active subunits (colored brown) share an intracellular GT and a membrane-integrated domain. Alginate consists of mannuronic (yellow) and guluronic acid (green), cellulose of glucose (beige), PNAG of NAG (gray), chitin of NAG, and HA of NAG and GA (magenta) units. A dashed circle indicates the binding site for the signaling molecule cyclic-di-GMP. Lower panel: The enzymes catalyze the transfer of a nucleotide diphosphate (NDP)-activated sugar (black hexagon) to another glycosyl unit, thereby generate NDP as a second reaction product. Among the synthases shown, HAS is the only enzyme that appears to elongate the polymer at its reducing end, thereby generating an UDP-attached polysaccharide. OM, IM: Outer and inner membrane.