Figure 4.
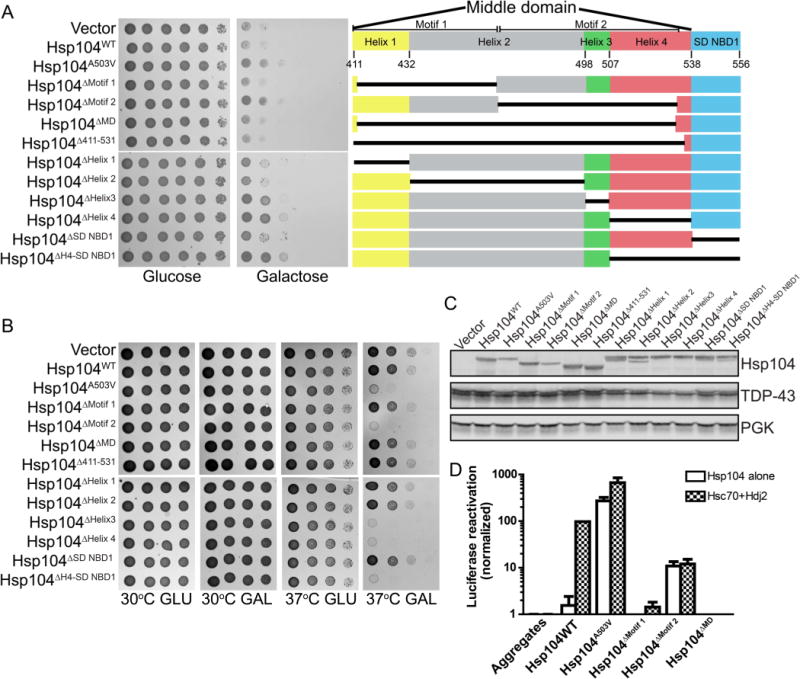
Deletion of Hsp104 MD motifs and helices. Deletion of MD motif 2, helix 3, or helix 4 potentiates Hsp104. (A) W303Δhsp104 yeasts integrated with pAG303GAL-TDP-43 were transformed with the indicated 416GAL-Hsp104 deletion construct, empty plasmid, Hsp104WT, or Hsp104A503V. Strains were serially diluted 5-fold and spotted on glucose (off) or galactose (on) media (left). Organization of the middle domain and small domain of NBD1 (right). (B) W303Δhsp104 yeasts were transformed with the indicated 416GAL-Hsp104 plasmid or empty vector control. Yeasts were grown to saturation in synthetic raffinose medium, serially diluted, and spotted onto SD-Ura or SGal-Ura media and incubated at 30 or 37 °C. Plates were analyzed after 2–3 days of growth. (C) Selected strains from A were induced for 5 h, lysed, and immunoblotted. 3-Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) serves as a loading control. (D) Luciferase aggregates were incubated with the purified Hsp104 variants (0.167 μM hexamer) plus (checkered bars) or minus (clear bars) Hsc70 (0.167 μM) and Hdj2 (0.167 μM). Values represent means ± SEM (n = 3).
