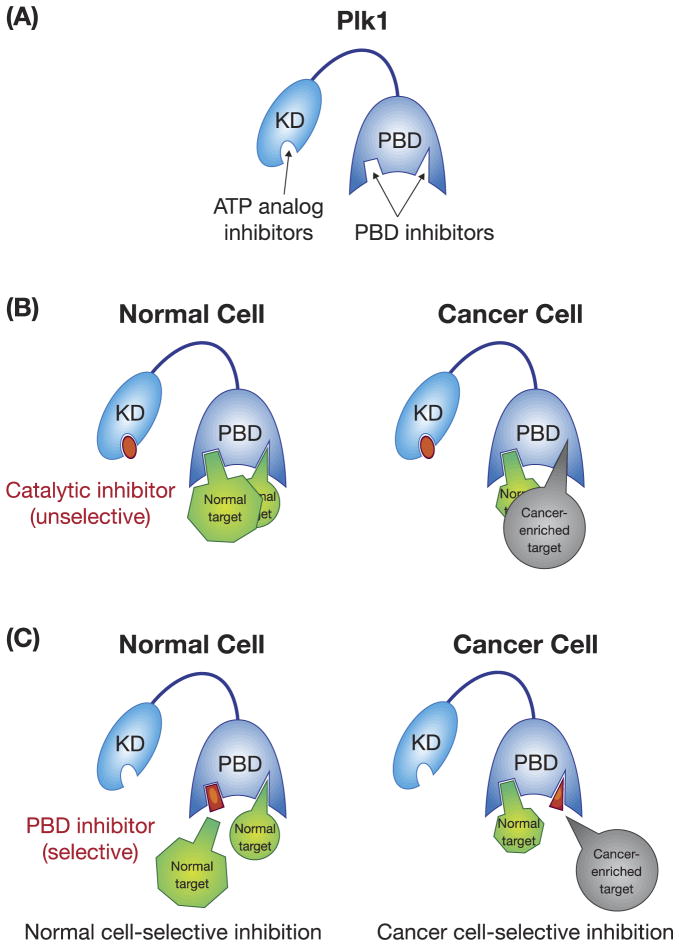
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram showing two strategies that target either the catalytic activity or the PBD of Plk1. (A) The catalytic activity of Plk1 is mostly targeted by ATP-competitive inhibitors, while the PBD is inhibited by PBD-binding antagonists. K.D., kinase domain; PBD, polo-box domain. (B) Catalytic inhibitors are unselective because they can abolish the catalytic activity of Plk1 in both normal and cancer cells. (C) PBD inhibitors can be designed in such a way that they can selectively inhibit cancer cell–enriched PBD-dependent interactions. The normal and cancer-enriched targets are drawn in different sizes in (B) and (C) to indicate altered levels of PBD-dependent interactions between normal and cancer cells.