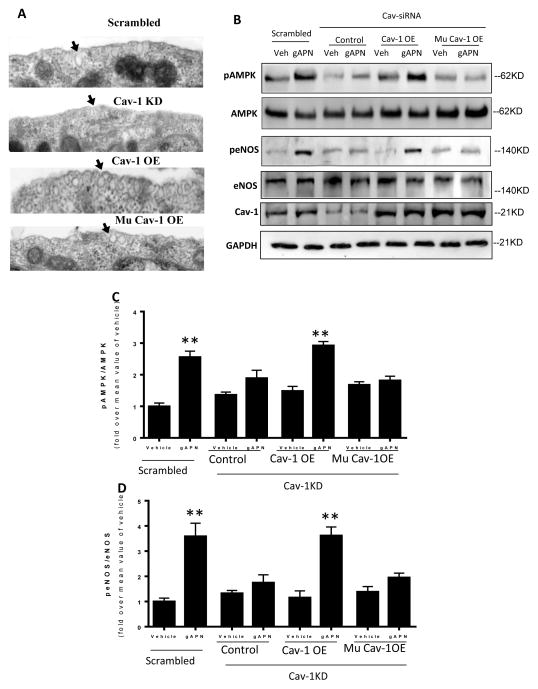
Figure 7.
Knock-in of a wild type Cav1 (Cav1-OE) in Cav1 knock-down cells restored caveolae structure (A) and rescued APN signaling as determined by AMPK and eNOS phosphorylation (B, C, D). In contrast, knock-in of a mutated Cav1 scaffolding domain (Mu Cav1-OE) restored caveolae structure (A), but failed to rescue APN signaling in Cav1 knock-down cells (B, C, D). Arrows in panel A indicate caveolae structures in the cell surface. N=6–8 dishes/group from at least 4 different cell batches. **P<0.01 vs. respective control.