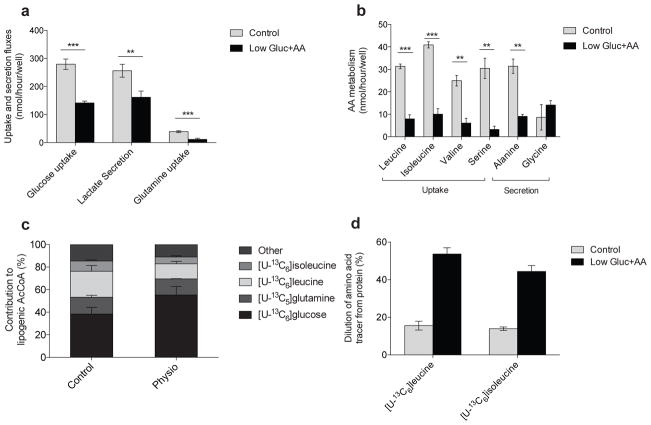
Figure 4. BCAA utilization is supported by protein catabolism.
(a) Uptake and secretion fluxes in 3T3–L1 adipocytes cultured in control and Low Gluc+AA media.
(b) Amino acid uptake and secretion in control and Low Gluc+AA media.
(c) Contribution of each tracer to lipogenic AcCoA in 3T3–L1 adipocytes cultured in control and Low Gluc+AA media. BCAA contributions were adjusted to account for dilution of intracellular amino acids from protein turnover using the average BCAA labeling over the course of the experiment. Glutamine dilution occurred primarily via glucose–derived synthesis.
(d) Percent of pool without label when cultured in indicated tracer substrate in control and Low Gluc+AA for 24 hours.
Data presented in (a)–(d) represent mean ± s.d., except (c) which represents model output ± 95% c.i. Data shown in (a)–(b) are 3 technical replicates representative of 3 biological replicates; **represents p<0.01 and *** represents p<0.001 by Student’s two–tailed t–test.