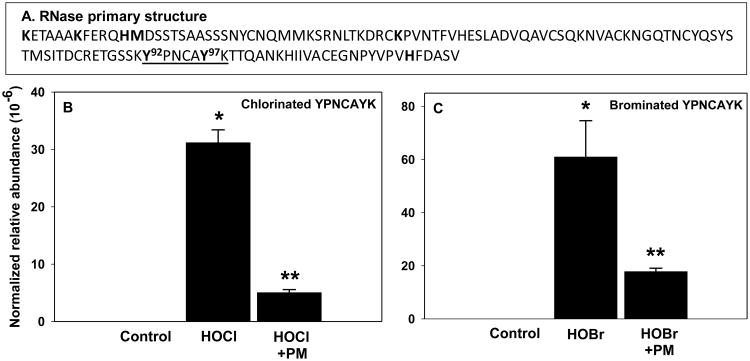
Figure 3.
Halogenation of functionally important RNase residues Y92 and Y97 and protection by PM. Location of key functional sites (bold font) and tryptic YPNCAYK peptide (underlined) within RNase sequence (A). RNase (50 μg/mL) was modified with either 60 μM HOCl (B) or 60 μM HOBr (C) with or without 60 μM PM and analyzed using LC-MSMS as described under Experimental procedures. Normalized relative abundance = sum of all modified forms of YPNCAYK peptide/average of three internal standard peptides. *P<0.05, control vs. hypohalous acid (n=3); **P<0.05, hypohalous acid vs. hypohalous acid + PM (n=3).