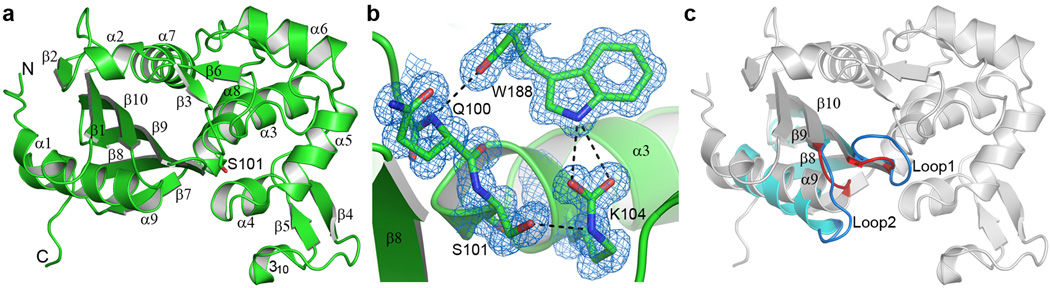
Figure 1. The BPU-1 structure.
(a) Ribbon representation of the BPU-1 crystal structure. The secondary structure assignment is indicated. The sidechain of the catalytic serine residue, Ser101, indicates the location of the enzyme active site. Single letter amino acid abbreviations are used throughout the Figures for clarity. (b) Final 2Fo-Fc electron density near the BPU-1 active site, contoured at 1.2σ. Electron density for the carboxylate moiety covalently attached to the side chain of Lys104 is evident. The carboxylated lysine is anchored by two hydrogen bonding interactions to a highly-conserved tryptophan residue (Trp188) from a loop adjacent to the active site. This loop is in turn anchored to the N-terminus of helix α3 by an additional hydrogen bonding interaction. (c) Superposition of BPU-1 (gray ribbons) and OXA-23 (cyan ribbons). Only strands equivalent to β8, β9, and β10, along with helix α9, are shown for OXA-23 for clarity. Two loops (Loop1 and Loop2) which show the largest structural deviation between BPU-1 and the OXA enzymes are shown in red for BPU-1 and blue for OXA-23.