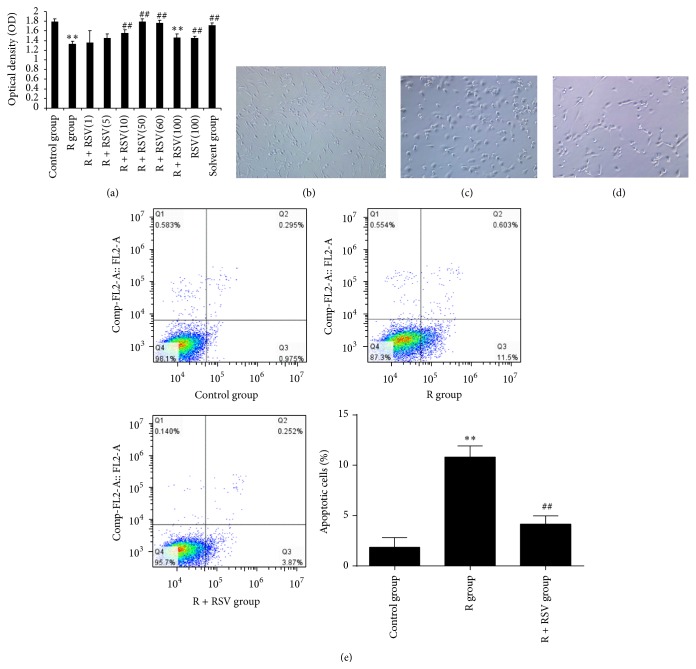
Figure 2.
Effects of resveratrol on PC12 cell viability, apoptosis, and morphology. (a) The results show that rotenone induces a statistically significant decrease in cell viability. Resveratrol significantly relieves the damage to PC12 cells induced by rotenone within a concentration range (5–100 µM). When the concentration is under 5 μM, the protective effect is not significant. Protection is concentration-dependent; however, at a concentration of 100 μM, the protective effect of resveratrol on PC12 cell viability was decreased compared to 60 μM. (b) The normal (control) morphology of PC12 cells with long processes. (c) The processes of PC12 cells in the R group appear much shorter compared with that of the control group. (d) The injury to PC12 cell morphology was alleviated with resveratrol pretreatment. (e) Results show that rotenone induces an increase of cell apoptosis with statistical significance. Resveratrol pretreatment decreases the number of apoptotic cells induced by rotenone with significant difference. The results are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. ∗∗ P < 0.01 versus control group; ## P < 0.01 versus R group.