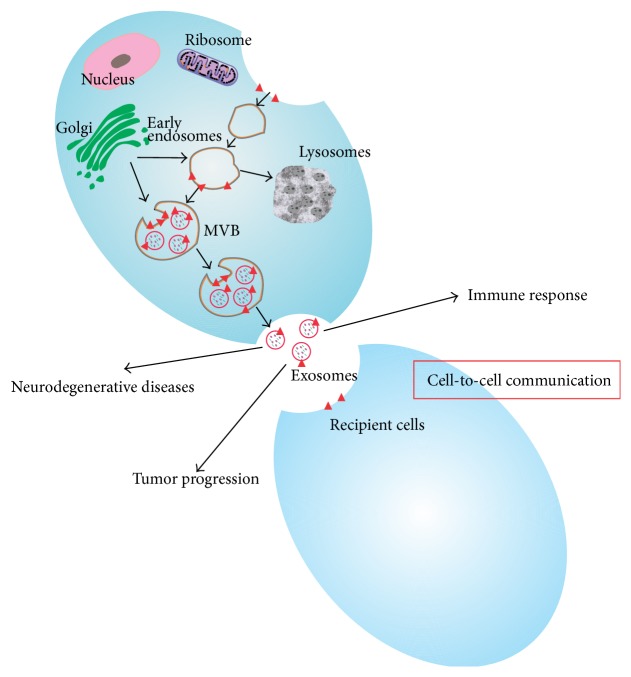
Figure 1.
Biogenesis and action of exosomes. Exosomes are formed by inward budding of membrane of the multivesicular bodies (MVBs); when MVBs fused with the membranes, the exosomes are released. Exosomes can deliver lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid to recipient cells when circulating in the extracellular space. Exosomes are important mediators of intercellular communication and play significant roles in immune response, tumor progression, and neurodegenerative disease among others.