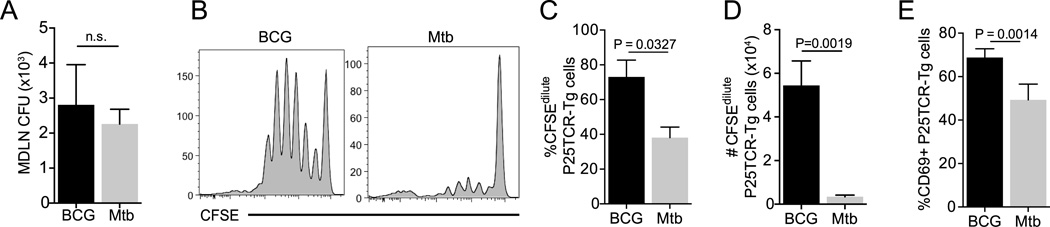
Figure 3.
Superior in vivo priming of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells by M. bovis BCG compared to M. tuberculosis when the number of bacteria is equivalent. Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (105/mouse) infected with M. bovis BCG or M. tuberculosis H37Rv (MOI, 2) were administered intratracheally to mice that also received CFSE-labeled P25TCR-Tg CD4+ T cells intravenously. (A) Quantitation of M. bovis BCG or M. tuberculosis CFU in lung-draining lymph nodes 60 h after iintratracheal transfer. (B) Representative CFSE dilution plots from M. bovis BCG- or M. tuberculosis-infected mice. (C) Frequency and (D) total number of CFSEdilute P25TCR-Tg cells in lung-draining lymph nodes. (E) Frequency of P25TCR-Tg CD4+ cells expressing CD69 in M. bovis BCG- or M. tuberculosis-infected mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Student t test was performed to compare M. tuberculosis- and M. bovis BCG-infected samples.