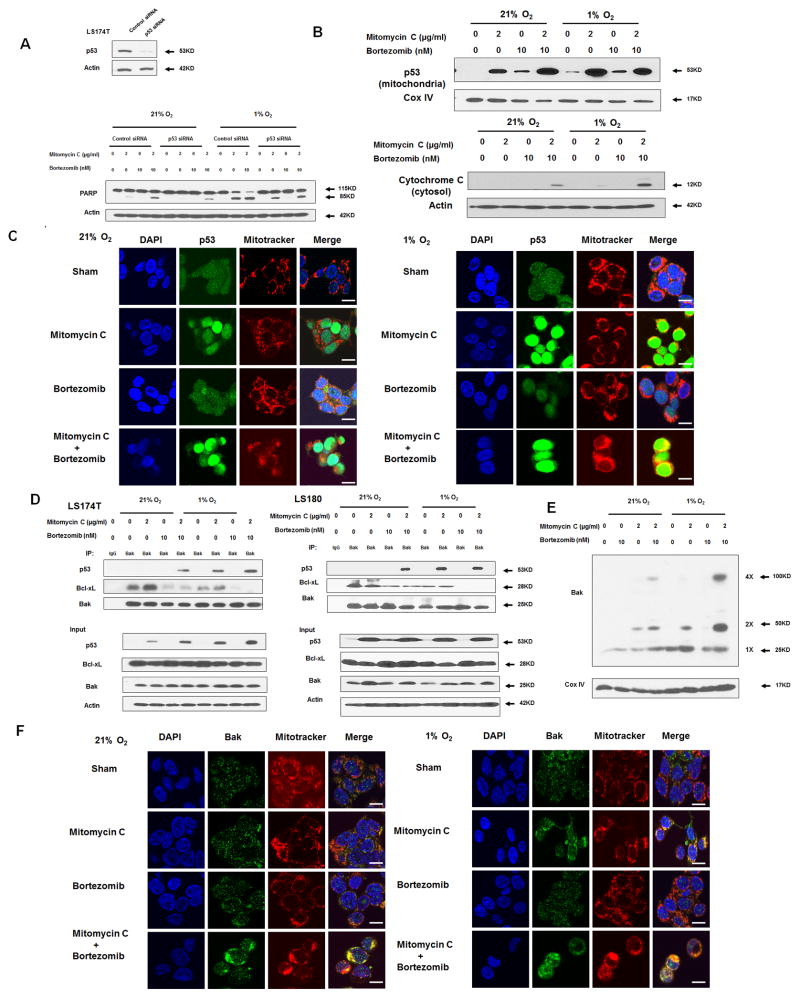
Figure 5. Role of p53 in the combinatorial treatment with mitomycin C and bortezomib under normoxia and hypoxia.
(A) LS174T cells were transfected with control siRNA or p53 siRNA for 48 h and the level of p53 was detected by immunoblotting (inset). After 48 h transfection, cells were treated with mitomycin C (2 μg/ml) and/or bortezomib (10 nM) under normoxia and hypoxia for 24 h (main). PARP was detected with immunoblotting. The levels of p53 were detected by immunoblotting 72 h after transfection. Actin was used as a loading control. (B) LS174T cells were treated with mitomycin C (2 μg/ml) and/or bortezomib (10 nM) under normoxia and hypoxia for 24 h. After treatment, cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were isolated and p53 was detected in mitochondrial fractions with immunoblotting. The results of the COX IV analysis are shown as an internal mitochondrial control. Actin was used as an internal cytosol control. (C) After treatment, mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker. p53 was stained with anti-p53 antibody. Localization of p53 was examined by confocal microscope. Scale bar 15 μm. (D) LS174T cells and LS180 cells were treated with mitomycin C (2 μg/ml) and/or bortezomib (10 nM) under normoxia and hypoxia for 24 h. After treatment, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Bak antibody or IgG and immunoblotted with anti-p53 and anti-Bcl-xL antibody. The presence of Bak, p53 and Bcl-xL in the lysates was examined. (E) LS174T cells were treated with mitomycin C (5 μg/ml) and/or bortezomib (10 nM) in normoxia and hypoxia for 24 h. After treatment, mitochondria were isolated, cross-linked with 1 mM dithiobis (succinimidyl propionate) and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Bak antibody. Bak monomer (1X) and multimers (2X and 4X) are indicated. COX IV was used as a mitochondrial marker. Scale bar 15 μm. (F) After treatment, mitochondria were stained with MitoTracker. Bak was stained with anti-Bak antibody. Localization of Bak was examined under confocal microscope.