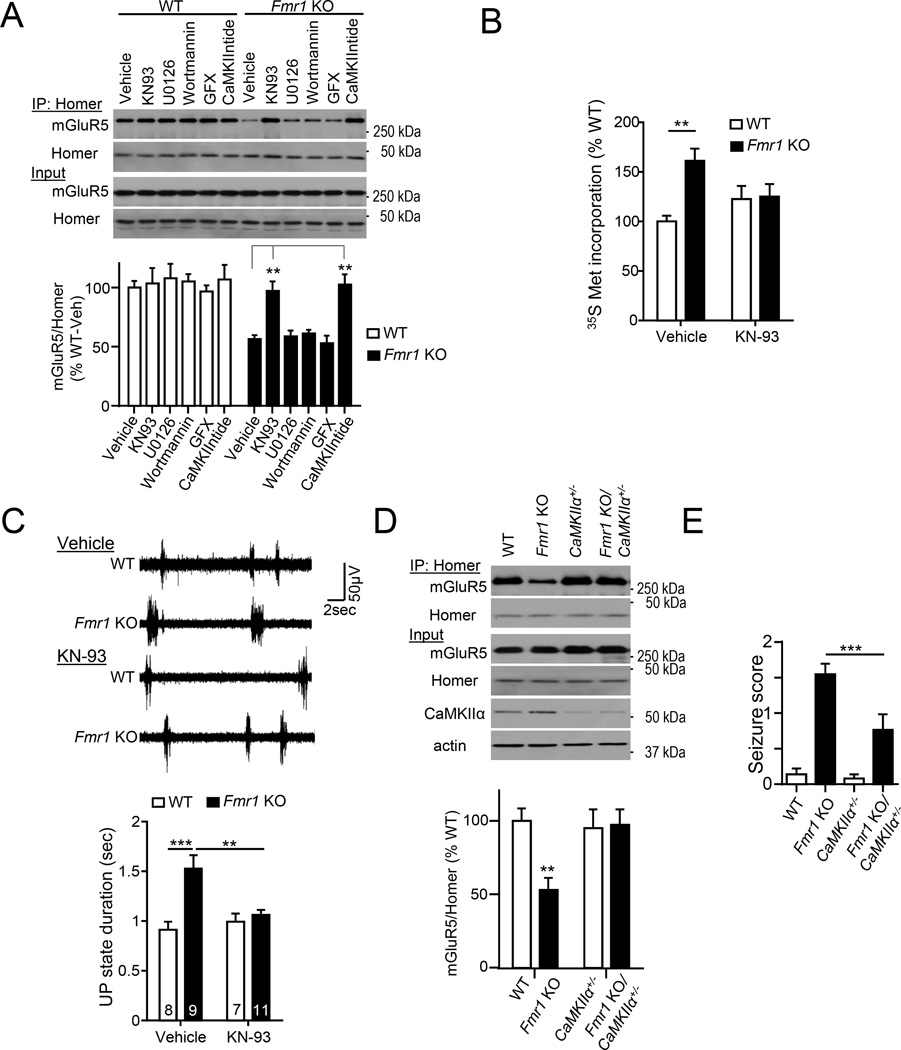
Figure 6. Genetic or pharmacological reduction in CaMKIIα activity rescues mGluR5-Homer scaffolds and other phenotypes associated with Fragile X Syndrome.
A) Inhibition of CaMKII activity (KN93 or CaMKIINtide) restores mGluR5-long Homer interaction in Fmr1 KO neocortical neurons. Inhibitors of other kinases (ERK, PI3K or PKC) have no effect. Blots of mGluR5 after co-IP with Homer. n=4 cultures/genotype.
B) Acute inhibition of CaMKII activity by KN93 treatment rescues enhanced basal translation rates in Fmr1 KO hippocampal slices as measured by 35S Met incorporation into total protein. n = 8 mice/ genotype.
C) Acute Inhibition of CaMKII activity by KN93 rescues prolonged neocortical UP states in Fmr1 KO neocortical slices. Left: Representative traces of UP states from each condition. Scale bar = 50 µV/ 2sec.
D) Genetic reduction of CaMKIIα in Fmr1 KO/CaMKIIα+/− mice rescues mGluR5-Homer interaction in Fmr1 KO mice. The front cortex tissue lysates were from WT/WT, Fmr1 KO/WT, WT/CaMKIIα+/- and Fmr1 KO/CaMKIIα+/− mice. Western blots of mGluR5 after coimmunoprecipitation (IP) with Homer antibody (top). Input was shown on the bottom, antibody as indicated. n = 4 mice/genotype
E) Cross Fmr1 KO mice and CaMKIIα+/− mice rescues audiogenic seizures. Fmr1 KO mice had an increased seizure score, the audiogenic seizure score was reduced in Fmr1 KO/CaMKIIα+/− mice (n = 35, 37, 28 and 21 mice for WT/WT, Fmr1 KO/WT, WT/CaMKIIα+/− and Fmr1 KO/CaMKIIα+/−, respectively).
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. See also Figure.S5