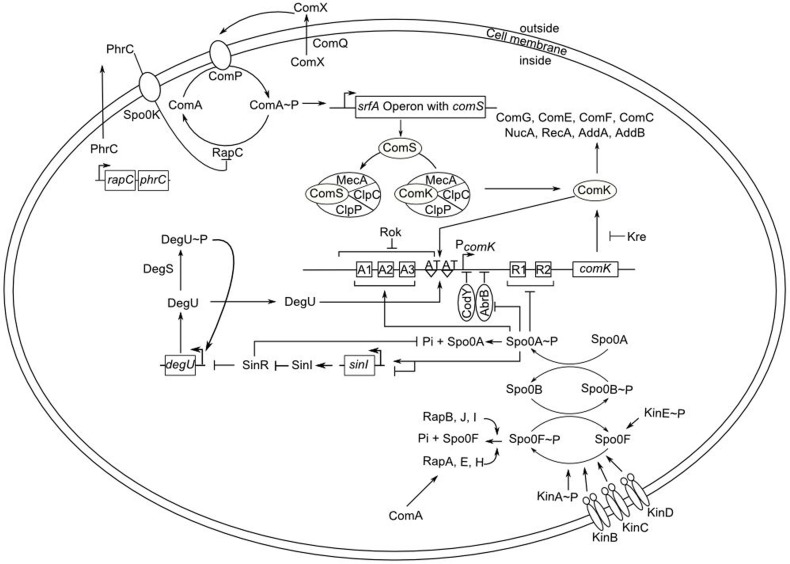
Figure 1.
Overview of competence regulation in B. subtilis. Lines ending in perpendiculars and arrows denote negative and positive effects, respectively. The quorum sensing mechanism containing the modified peptide ComX results in phosphorylation of the ComA response regulator by ComP. ComA~P activates the transcription of the srf operon with the embedded comS gene. ComS binds to the protease complex of MecA, ClpC, and ClpP and prevents the degradation of the transcription factor ComK. The stability of the comK mRNA is also influenced by Kre. The transcription of comK is regulated by various factors. ComK activates its own expression by binding to the AT-boxes in its promoter region. This binding is facilitated by DegU. At low concentration, Spo0A~P binds to three special sequences (A1–A3; high affinity binding sites) in the promotor of comK. At high concentration, Spo0A~P is capable of binding to further sequences (R1 and R2; low affinity binding sites) and repressing the expression of comK. Spo0A~P also release the comK expression by repressing AbrB. Other repressing factors of the comK expression are CodY and Rok. Rap proteins, such as RapA, prevent ComA~P interaction with its target DNA and dephosphorylate Spo0F~P. The expression of sinI is activated at the low level of Spo0A~P and repressed by a high level of Spo0A~P concentration. SinI antagonizes SinR, which represses the expression of degU. Finally, high concentration of ComK activates the expression of genes for DNA-uptake and -integration as well as many other genes.